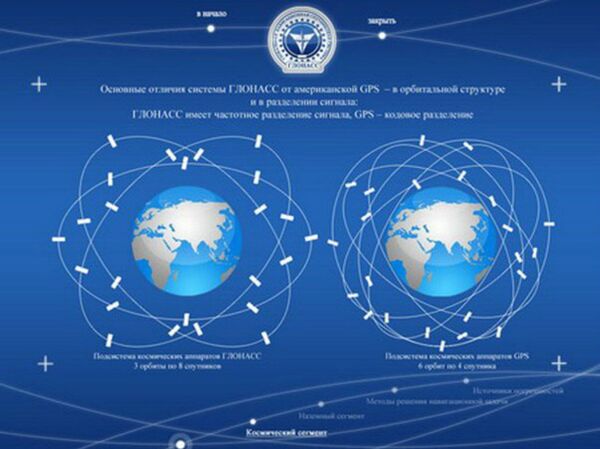
“Russia’s GLONASS system outperforms GPS in accuracy at northern latitudes, as it was originally developed for northern latitudes, unlike the US GPS, which was developed for southern latitudes. Besides, it covers the Earth with fewer satellites. Russia’s 24 satellites cover the same area as the 31 [used by] the US,” the director of Titov Main Test and Space Systems Control Centre, Major General Andrey Ilyin said on Saturday.
He also added that the number of satellites within Russia’s GLObal NAvigation Satellite System (GLONASS) will remain the same, even though it will get more advanced satellites.
“The number of operating satellites will remain unchanged, 24, but the bandwidth and data transfer speed will increase due to the new advanced equipment,” he added.
Russia’s GLONASS currently incorporates a network of 28 satellites. 24 actually cover the earth, one is being kept in orbital reserve, one is being researched on by engineers, and two 'GLONASS-K' satellites are undergoing tests and are set to enter the services soon afterwards.
GPS (The Global Positioning System) was developed by the US and has a network of 31 satellites covering the same area across the planet.
The image shows the orbit and constellation of GLONASS (left) and GPS (right).
The development of GLONASS began in the Soviet Union in 1976.
Beginning on October 12, 1982, numerous rocket launches added satellites to the system until the constellation was completed in 1995. After a decline in capacity during the late 1990s, in 2001, under Vladimir Putin's presidency, the restoration of the system was made a top government priority and funding was substantially increased.
By 2010, GLONASS had achieved 100% coverage of Russia's territory and in October 2011, the full orbital constellation of 24 satellites was restored, enabling full global coverage. The GLONASS satellites' designs have undergone several upgrades, with the latest version being GLONASS-K.

Today every smartphone, regardless of its price or level of sophistication, is equipped with A-GPS (assisted Global Positional System) which uses the mobile telephony network's capabilities to find your location.
Now with GLONASS being offered for public services, more and more smartphones are being launched with GPS+GLONASS technology, which uses a dual-core location-based service to find their location.
More and more companies and chip manufacturers seem to be interested in GLONASS technology, so more and more smartphones are expected to be launched with this technology.
Currently up to 151 smartphone manufacturers, including Apple, Samsung, HTC, Motorola, Sony, Nokia, among others, support GLONASS