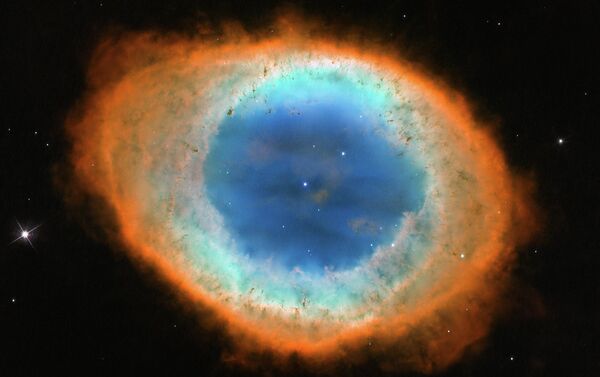
The image of intricate swirls of gas offer a glimpse of the Sun's distant future. In 5 billion years' time, it will be dying and is expected to behave in the same way as in the main image shown, shedding its outer layers to reveal the burning core, which then becomes a slowly cooling ember known as a white dwarf.
As a star ages, the nuclear reactions that keep it shining begin to falter. This uncertain energy generation causes the stars to pulsate in an irregular way, casting off its outer layers into space. As the star sheds these outer gases, the super-hot core is revealed. It gives off huge quantities of ultraviolet light, and this radiation causes the gas shells to glow, creating the fragile beauty of the nebula.
The most distant #galaxy to date discovered by astronomers https://t.co/1tRFr0uzSo #NASA #astronomy pic.twitter.com/5kwLoONj3a
— Sputnik UK (@SputnikNewsUK) March 4, 2016
The main image shows the planetary nebula Kohoutek 4-55, which is named after its discoverer, the Czech astronomer Luboš Kohoutec, and located 4600 light years from Earth, in the direction of the constellation Cygnus. A planetary nebula is formed from material in the outer layers of a red giant star that were expelled into interstellar space when the star was in the late stages of its life. Ultraviolet radiation emitted from the remaining hot core of the star ionises the ejected gas shells, causing them to glow.
This image was the final 'pretty picture' taken by the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2). The camera was installed in 1993 and worked until 2009, offering a 16-year stretch of unparalleled observations.
WFPC2 took many of Hubble's iconic images. They helped to make the space telescope a household name across the world.

This turbulent cosmic pinnacle lies within a tempestuous stellar nursery called the Carina Nebula, located 7,500 light-years away in the southern constellation Carina. The image celebrates the 20th anniversary of Hubble's launch and deployment into an orbit around Earth.
Scorching radiation and fast winds (streams of charged particles) from super-hot newborn stars in the nebula are shaping and compressing the pillar, causing new stars to form within it. Streamers of hot ionized gas can be seen flowing off the ridges of the structure, and wispy veils of gas and dust, illuminated by starlight, float around its towering peaks. The denser parts of the pillar are resisting being eroded by radiation much like a towering butte in Utah's Monument Valley withstands erosion by water and wind.
Nestled inside this dense mountain are fledgling stars. Long streamers of gas can be seen shooting in opposite directions off the pedestal at the top of the image. Another pair of jets is visible at another peak near the center of the image. These jets (known as HH 901 and HH 902, respectively) are the signpost for new star birth. The jets are launched by swirling disks around the young stars, which allow material to slowly accrete onto the stars' surfaces.
Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 observed the pillar on Feb. 1-2, 2010. The colors in this composite image correspond to the glow of oxygen (blue), hydrogen and nitrogen (green), and sulfur (red).



This turbulent cosmic pinnacle lies within a tempestuous stellar nursery called the Carina Nebula, located 7,500 light-years away in the southern constellation Carina. The image celebrates the 20th anniversary of Hubble's launch and deployment into an orbit around Earth.
Scorching radiation and fast winds (streams of charged particles) from super-hot newborn stars in the nebula are shaping and compressing the pillar, causing new stars to form within it. Streamers of hot ionized gas can be seen flowing off the ridges of the structure, and wispy veils of gas and dust, illuminated by starlight, float around its towering peaks. The denser parts of the pillar are resisting being eroded by radiation much like a towering butte in Utah's Monument Valley withstands erosion by water and wind.
Nestled inside this dense mountain are fledgling stars. Long streamers of gas can be seen shooting in opposite directions off the pedestal at the top of the image. Another pair of jets is visible at another peak near the center of the image. These jets (known as HH 901 and HH 902, respectively) are the signpost for new star birth. The jets are launched by swirling disks around the young stars, which allow material to slowly accrete onto the stars' surfaces.
Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 observed the pillar on Feb. 1-2, 2010. The colors in this composite image correspond to the glow of oxygen (blue), hydrogen and nitrogen (green), and sulfur (red).
This particular shot is a composite of three images, each taken at a specific wavelength to isolate the light coming from particular atoms of gas. The different wavelengths have been color-coded to aid recognition. Red signifies nitrogen gas, green shows hydrogen and blue represents oxygen.


