"On November 30, 2017, the Council adopted Decision (CFSP) 2017/2214 in order to permit certain operations concerning hydrazine (CAS 302-01-2) in concentrations of 70 % or more, which is included in the Common Military List of the European Union," the Council of the European Union's regulation in the Official Journal of the European Union reads.
According to the council, the substance is necessary for the flight of the ExoMars carrier module and tests and flight of the ExoMars descent module under the umbrella of the ExoMars 2020 mission.
The EU Common Military List regulates the scope of military items controlled for export in the EU pursuant to the EU Common Position on arms exports.
The sanctions were introduced under the 2015 amendment order, imposing sanctions on Russia over events in Ukraine.
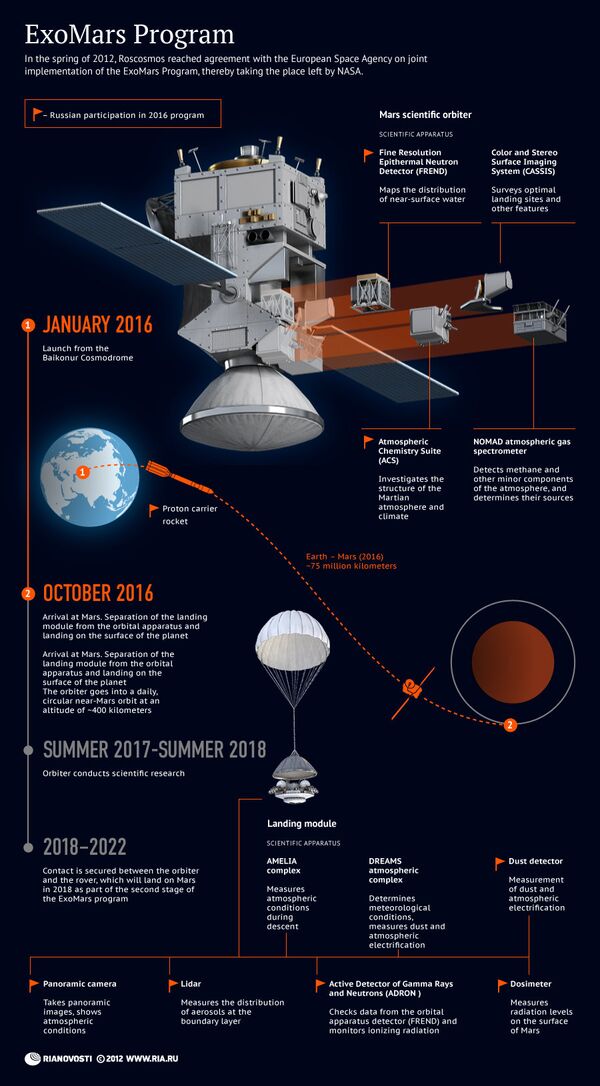
ExoMars Mission
The ExoMars mission aims to find the confirmation of the existence of life on Mars.
Who'd have thought that prep for @ESA_ExoMars included a crash course in #Geology? A recent field trip explains all https://t.co/bzLEOAmmqf pic.twitter.com/6zsgJ5TSgE
— UK Space Agency (@spacegovuk) 10 октября 2017 г.
The first mission of the program started with the launch of a Russian four-stage Proton-M/Breeze-M launch vehicle on March 14, 2016 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome and included a Schiaparelli module and the Trace Gas Orbiter, which delivered the module to Mars.
#OTD last year, I arrived in #Mars orbit! #ExoMars https://t.co/UWCoyE5Sw2
— ExoMars orbiter (@ESA_TGO) 19 октября 2017 г.
The second module is expected to be launched in 2020, carrying a drill and tools for exobiology and geochemistry research.
In his interview to Sputnik in April this year, ESA Director-General Jan Woerner stated that the agency was prepared to broaden cooperation with Russia. According to him, the first tests of various parts for the second ExoMars expedition planned for 2020 will begin no earlier than next year.