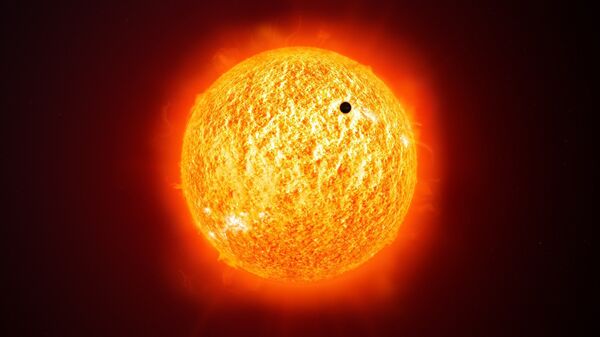
NASA has released dramatic images that point to the fact that the Sun may have already reached the solar minimum point in its regular cycle, as they have captured it looking extraordinarily blank with no visible sunspots whatsoever. The so-called “monster” solar prominence, which is when solar activity spirals up, was recorded by the US agency’s Solar Dynamic Observatory in 2011, with the pictures showing what we will witness when the Sun's minimum reaches its end.
Solar minimums are characteristic of a period of reduced activity on Earth’s star and occur once every 11 years. However, the reality is such that a calmer and almost peaceful appearance is deceptive as it may give rise to severe magnetic storms with the potential to change the gravitation of satellites, interfere with air travel, and even disrupt electrical grids.
“The sun has been without spots for 16 consecutive days–a sign that Solar Minimum is underway”, the website Space Weather wrote, going on to say that many would incorrectly think the solar minimum “is uninteresting”.
“This phase of the solar cycle brings extra cosmic rays and long-lasting holes in the sun's atmosphere”, the site went on.
To illustrate the general cooling that the solar minimum typically brings about, given the sun’s decreasing heating capacity, NASA cited an incident from between 1650 and 1710, arguing that Earth plunged into “a deep freeze” at the time. As Earth swung to a high number of sunspots in 2014, with the latter sometimes reaching the size of the planet Jupiter, NASA weighed in, estimating that the minimum would strike from 2019 to 2020. Climate change sceptics, meanwhile, eagerly refer to the solar minimum as an argument, hailing the cooling as evidence that the allegedly uncontrolled heating of our planet is showing signs of reversing.