On 12 June, President Joe Biden met with G7 leaders to discuss strategic competition with China and bring forward a new bold global infrastructure initiative – Build Back Better World (B3W). The plan envisages helping "narrow the $40+ trillion infrastructure need" in developing countries "from Latin America and the Caribbean to Africa to the Indo-Pacific," explaining that the G7 and other like-minded partners will mobilise "private-sector capital in four areas of focus," namely climate, health, and health security, digital technology, and gender equity and equality.
Why G7's B3W is No Challenge to BRI
It's obvious that the Biden-proposed endeavour is nothing less than a potential substitute to the Beijing-led Belt and Road Initiative, which has been implemented by China since 2013, South Asia observers say, expressing skepticism over the viability of the G7 project.
Firstly, B3W does not seem to serve the essential interest of developing countries as it's a US attempt "to export its surging internal inflation to the world" in the post-COVID era, according to The Global Times, a Chinese daily newspaper. The US and other G7 countries have had many chances to address the developing countries' infrastructural gaps before, but somehow they turned a blind eye to the problem, the media outlet notes.
"Taking the African countries as an example, they have been facing an annual infrastructure investment shortfall of $108 billion," Song Wei, an associate research fellow at the Chinese Academy of International Trade and Economic Cooperation, told the Chinese daily. "The shortfall has long become a major barrier for the development of the continent, and why didn't the G7 realise the demand earlier?"
Besides that, B3W appears to be aimed at maintaining the West's dominance over emerging economies, looking like "a strategic plan to win political influence on a very large scale," writes Matteo Giovannini, a member of the China Task Force at the Italian Ministry of Economic Development.
At the same time, judging from Biden's proposal, the aid will be attached to "intrusive conditionalities" regarding human rights, climate change, corruption, and the rule of law, remarks Middle East and South Asia expert Dnyanesh Kamat in his op-ed for Syndication Bureau, suggesting that developing countries would rather choose "China’s simplified and no-strings-attached BRI funding."

Secondly, it's unclear where exactly B3W funding will come from. Observers doubt that the G7 countries would fork out $40 trillion which is more than the combined 2020 GDP of the seven countries. Many developed economies are still struggling to overcome the lockdown-related recession. The UK Parliament noted in May that because of the COVID outbreak the budget's 2020/21 deficit reached £303 billion (14.3 percent of GDP) which is "a peacetime record."
For its part, the Biden administration is still unable to overcome the resistance of GOP deficit hawks and pass a set of the president's bold domestic "build back better" initiatives in US Congress. Biden's initial $2.3 trillion infrastructure plan then shrank to $1.7 trillion, while last Thursday, a bloc of Senate moderates proposed spending $974 billion over five years, or $1.2 trillion over eight years, according to Reuters.
Meanwhile, the White House's hint that "the private sector" could pay for B3W does not appear realistic, according to Tom Fowdy, a British political and international relations analyst.
"This is a logical contradiction in real terms, private enterprises invest where they will make a profit, not to meet the needs of a specific country as the BRI does or to comprehensively recreate a national economy like CPEC," Fowdy suggested in his article for CGTN, a Chinese English-language news service. "They are not willing to take 'risks,' which many BRI projects have done."
Thirdly, it's unclear who will do the job, notes The Global Times. While China has mastered itself in infrastructural projects over the past years, there is "the distinct technological gap" between the People's Republic and most of the Western countries when it comes to infrastructure construction, the Chinese daily insists.
When it comes to the US, it needs to fix its own old infrastructure "before thinking about being the promoter of renovation outside of the national borders," echoes Matteo Giovannini.
Meanwhile, Beijing has already signed cooperation agreements with 140 countries and 31 international organisations within the BRI framework with 1,100 construction projects being underway in Africa alone despite the pandemic, according to the media outlet. For his part, Fowdy cites the fact that China has already implemented a considerable part of its grand design, while the G7 club has a long way to go.

The People's Republic has already kicked off the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) stretching from the western Chinese city of Kashgar to Pakistan's Arabian Sea port of Gwadar.
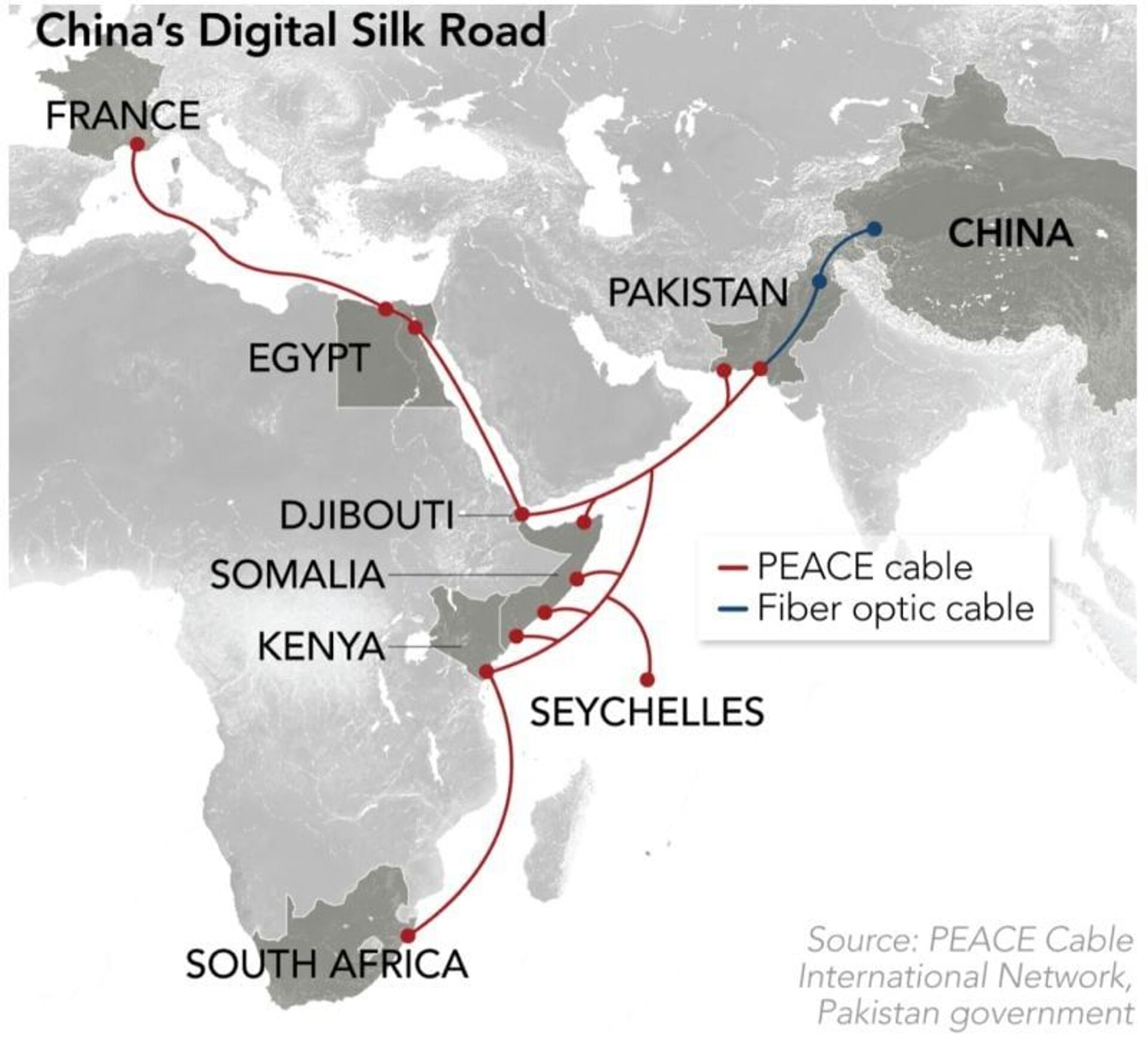
Transcontinental Eurasian and African railways are other examples of China's comprehensive effort. In addition, Beijing is also set to create the so-called Polar Silk Road in the Arctic, cooperating with Russia on employing the Northern Sea Route (NSR) – the shortest maritime lane from Europe to Asia. On top of this, China is implementing a Digital Silk Road, i.e. a network of subsea cables designed to bring Asia, Africa, and Europe together. Nothing of that kind has been made by G7 yet, observers point out.
Win-Win Solution Instead of Zero-Sum Game
Nevertheless, there is always room for consensus, argues Giovannini. He does not consider B3W as "a real challenge" for China, suggesting that the G7 initiative could become an opportunity to "alleviate some of the burden that China's scheme has so far carried on alone."
"Therefore, if the G7 countries are able to recalibrate their intentions to use the B3W as a vehicle for mutual prosperity instead of an instrument for challenging the status quo, and possibly for personal gain, then the whole international community will come out as a clear winner," the Italian scholar concludes.



