https://sputnikglobe.com/20230328/scientists-unearth-galactic-sized-black-hole--now-directly-facing-our-planet-1108869884.html
Scientists Unearth Galactic-Sized Black Hole Now Directly Facing Our Planet
Scientists Unearth Galactic-Sized Black Hole Now Directly Facing Our Planet
Sputnik International
A supermassive black hole has rotated, changing its direction, and now faces Earth, scientists have discovered.
2023-03-28T15:11+0000
2023-03-28T15:11+0000
2023-04-21T10:43+0000
science & tech
supermassive black hole
royal astronomical society
galaxy
milky way
https://cdn1.img.sputnikglobe.com/img/102429/55/1024295573_0:226:4000:2476_1920x0_80_0_0_e442f4aa6429cb9f63330d1e35e64af5.jpg
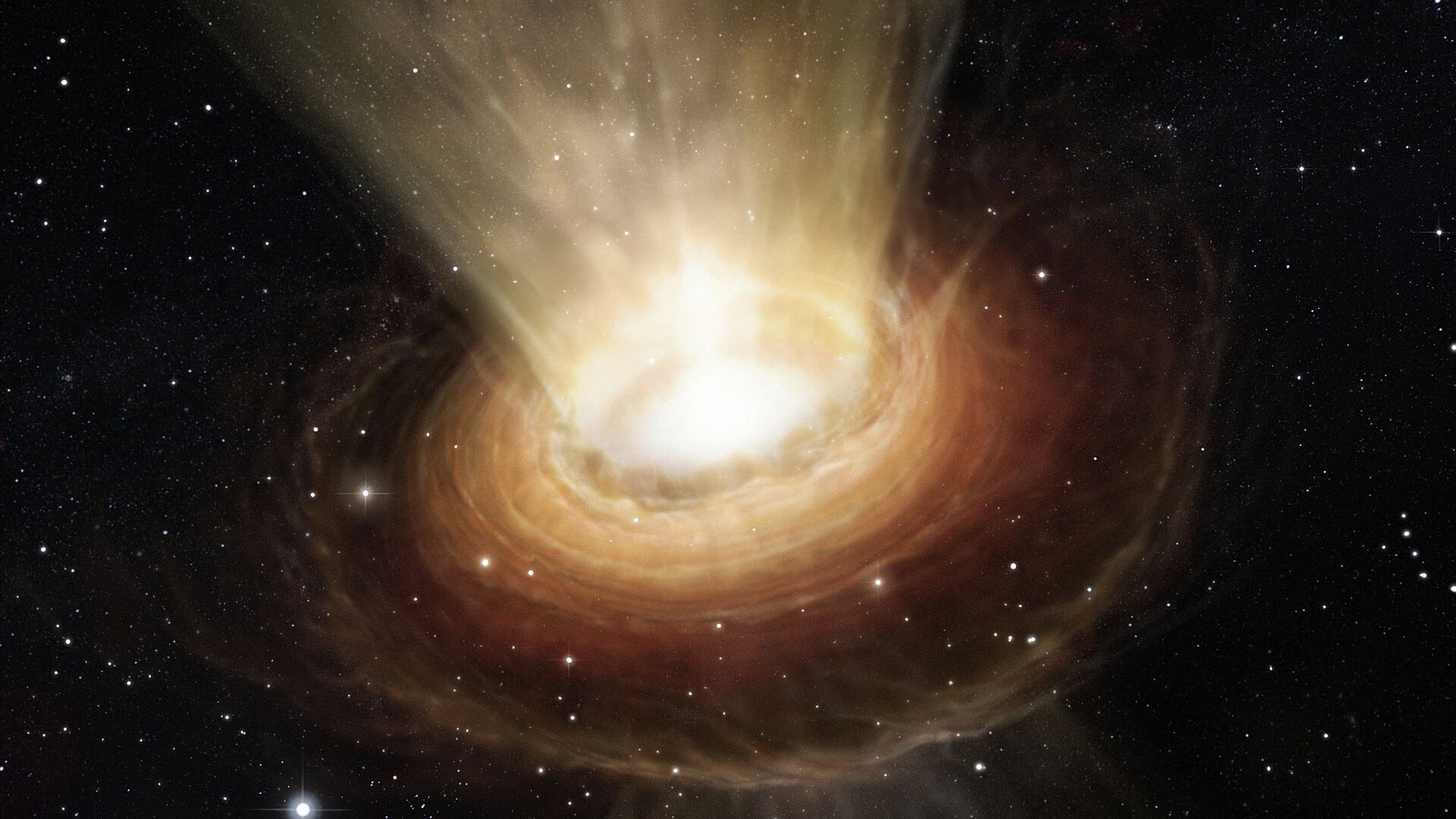
A recent stunning discovery by a team of scientists has left them both excited, but also rather concerned. The fact is, a supermassive black hole hidden away in a distant galaxy has changed its direction, swiveling by about 90 degrees, the international astronomers found.Situated 657 million light-years away in the PBC J2333.9-2343 galaxy, at the core of a “blazar”, this hole has changed its direction. Now, it is facing Earth, researchers at the Royal Astronomical Society discovered. Now, for those wondering what a blazar is, its a type of super-bright object called an active galactic nuclei (AGN) that is powered by such material as gas, dust, or stars falling onto it. Blazars generate relativistic jets comprised of ionized matter. In this case, the astronomers were observing the galaxy in question, classified as a radio galaxy, but found it to have odd characteristics. Resorting to a broad array of radio, optical, infrared, x-ray, ultraviolet and gamma ray telescopes, including Germany's 100m-Radio Telescope Effelsberg at the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy, the researchers studied the distant galaxy in electromagnetic spectrum. After they compared the properties of PBC J2333.9-2343 with other samples of blazars, the scientists concluded that this particular supermassive black hole's relativistic jet had shifted its direction.As to just what triggered this change in direction of the jets, scientists have speculated it could have been anything from a merger with another galaxy or object, to a strong burst of galactic nucleus activity. Further studies and observations will show just how this rotation of a black hole might impact our own galaxy - the Milky Way.
https://sputnikglobe.com/20220226/merging-waltz-caltech-finds-two-supermassive-black-holes-set-to-collide-warping-space--time-1093383738.html
https://sputnikglobe.com/20221015/milky-ways-ancient-heart-potentially-found-1101884166.html
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
2023
News
en_EN
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
supermassive black hole, has rotated, changing its direction, faces earth, scientists at the royal astronomical society, 657 million light-years away, pbc j2333.9-2343 galaxy,
supermassive black hole, has rotated, changing its direction, faces earth, scientists at the royal astronomical society, 657 million light-years away, pbc j2333.9-2343 galaxy,
Scientists Unearth Galactic-Sized Black Hole Now Directly Facing Our Planet
15:11 GMT 28.03.2023 (Updated: 10:43 GMT 21.04.2023) An international team of scientists at the Royal Astronomical Society can boast of having made a groundbreaking discovery regarding a galaxy situated 657 million light-years away from our planet Earth. After noticing the galaxy's peculiar properties, they undertook further observations.
A recent stunning discovery by a team of scientists has left them both excited, but also rather concerned. The fact is,
a supermassive black hole hidden away in a distant galaxy has changed its direction, swiveling by about 90 degrees, the international astronomers found.
Situated 657 million light-years away in the
PBC J2333.9-2343 galaxy, at the core of a “blazar”, this hole has changed its direction. Now, it is facing Earth,
researchers at the Royal Astronomical Society discovered.
Now, for those wondering what a
blazar is, its a type of super-bright object called an active galactic nuclei (AGN) that is powered by such material as gas, dust, or stars falling onto it.
Blazars generate relativistic jets comprised of ionized matter. 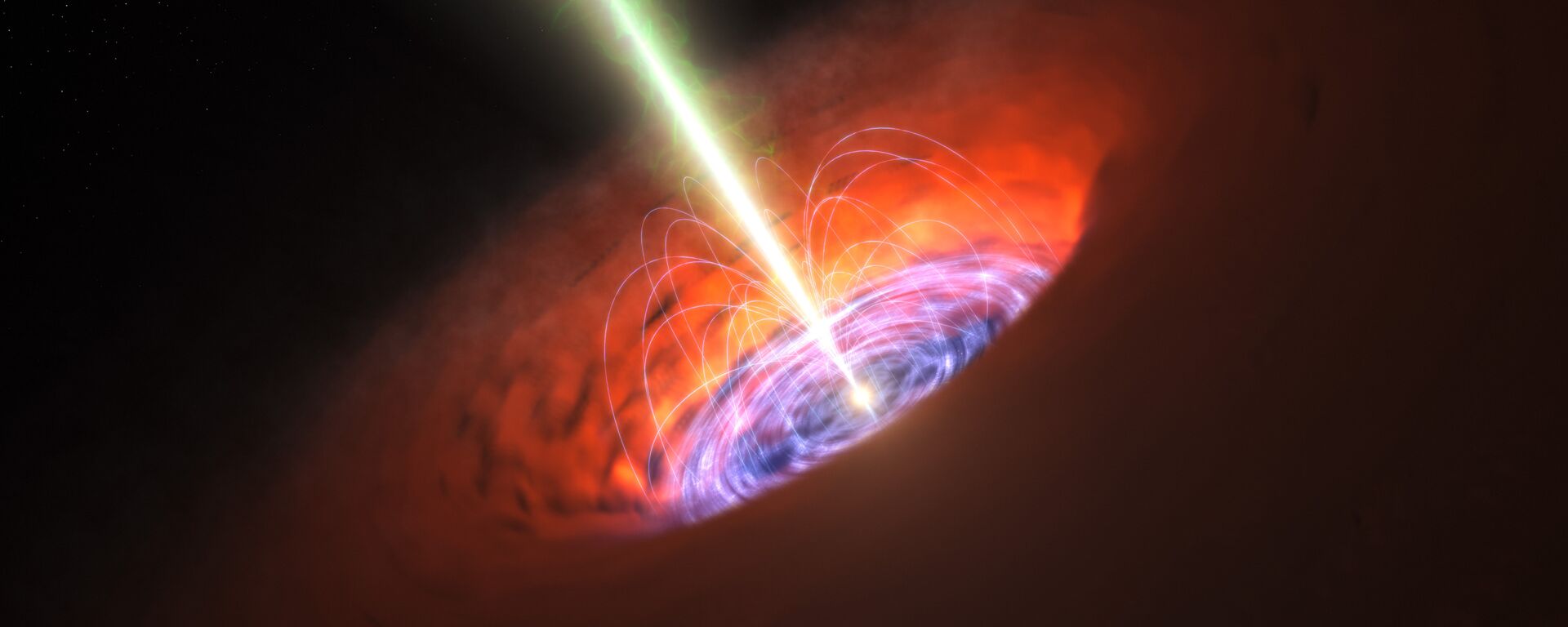
26 February 2022, 03:30 GMT
In this case, the astronomers were observing the galaxy in question, classified as
a radio galaxy, but found it to have odd characteristics. Resorting to a broad array of radio, optical, infrared, x-ray, ultraviolet and gamma ray telescopes, including Germany's 100m-Radio Telescope Effelsberg at the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy, the researchers studied the distant galaxy in electromagnetic spectrum.
After they compared the properties of PBC J2333.9-2343 with other samples of blazars, the scientists concluded that this particular supermassive black hole's relativistic jet had shifted its direction.
"We started to study this galaxy as it showed peculiar properties. Our hypothesis was that the relativistic jet of its supermassive black hole had changed its direction, and to confirm that idea we had to carry out a lot of observations,” Dr. Lorena Hernández-García, researcher at the Millenium Institute of Astrophysics and lead author of the study, told the press.
As to just what triggered this change in direction of the jets, scientists have speculated it could have been anything from a merger with another galaxy or object, to a strong burst of galactic nucleus activity. Further studies and observations will show just how this rotation of a black hole might impact our own galaxy -
the Milky Way.

15 October 2022, 17:04 GMT



