https://sputnikglobe.com/20231112/new-approach-to-pancreatic-cancer-treatment-shows-promise-for-survival-1114896492.html
New Approach to Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Shows Promise for Survival
New Approach to Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Shows Promise for Survival
Sputnik International
Pancreatic cancer is known for being very hard to treat. It has a low survival rate, with only 12 percent of patients living for a year and just 9 percent can survive for five years.
2023-11-12T12:06+0000
2023-11-12T12:06+0000
2023-11-12T12:06+0000
beyond politics
cancer
research
vaccine
https://cdn1.img.sputnikglobe.com/img/102283/29/1022832948_0:55:1040:640_1920x0_80_0_0_c0fa0f8445eea800c17fa460a60bc2e3.jpg
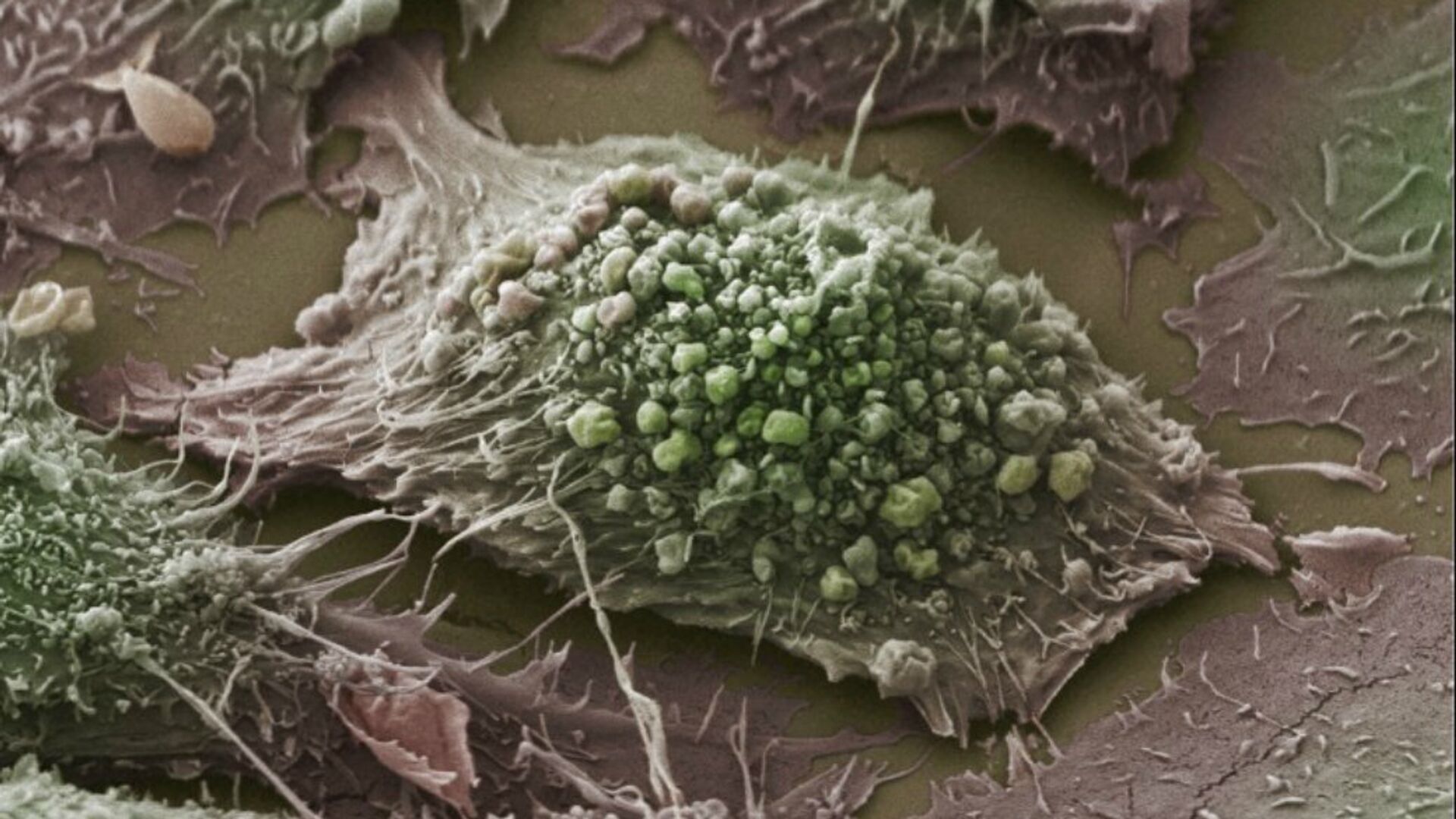
Preclinical studies conducted by the VCU Massey Comprehensive Cancer Center and the VCU Institute of Molecular Medicine in Virginia in the United States have demonstrated that polyinosine–polycytidylic acid (pIC), when directly administered to cancer cells, effectively inhibits tumor development and triggers malignant cell death. This research was recently published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.Mice with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumors, which closely mimic human pancreatic cancer, exhibited significantly improved survival rates after the implementation of a coordinated therapeutic plan. This promising approach, which harnesses the immune system offers hope for human pancreatic cancer patients.The research show that pIC, a substance that boosts the immune system, increases the chances of survival in lab animals with pancreatic cancer. It's safe for normal pancreatic cells and might improve survival for people with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a type of pancreatic cancer, either when used alone or in combination with conventional treatments such as gemcitabine.PDAC is known for being very hard to treat. It has a low survival rate, with only 12 percent of patients living for a year and just 9 percent surviving for five years. The research team established that a coordinated therapeutic plan significantly improved survival rates in mice with PDAC tumors, which closely resemble human pancreatic cancer. By using polyethyleneimine (PEI) to deliver pIC into the intracellular environment of tumor cells, the researchers have successfully stimulated cancer cell death.The research found that pretreating mice with pIC before cancer development reduced tumor growth by approximately 60 percent, suggesting a potential protective, vaccine-like effect. Further research is needed to explore its implications for cancer prevention.The study's promising results for treating pancreatic cancer suggest that this approach could potentially be used for various cancer types in conjunction with standard care.
https://sputnikglobe.com/20230815/study-reveals-useless-thymus-gland-may-greatly-reduce-cancer-risk-1112626826.html
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
2023
Chimauchem Nwosu
https://cdn1.img.sputnikglobe.com/img/07e7/09/01/1113046371_0:99:1536:1635_100x100_80_0_0_9c5c627283eca931c39fe4852bbb301c.jpg
Chimauchem Nwosu
https://cdn1.img.sputnikglobe.com/img/07e7/09/01/1113046371_0:99:1536:1635_100x100_80_0_0_9c5c627283eca931c39fe4852bbb301c.jpg
News
en_EN
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Chimauchem Nwosu
https://cdn1.img.sputnikglobe.com/img/07e7/09/01/1113046371_0:99:1536:1635_100x100_80_0_0_9c5c627283eca931c39fe4852bbb301c.jpg
polyinosine–polycytidylic acid (pic), pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (pdac), pancreatic cancer, polyethyleneimine (pei), intracellular environment of tumor cells, gemcitabine, cancer prevention.
polyinosine–polycytidylic acid (pic), pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (pdac), pancreatic cancer, polyethyleneimine (pei), intracellular environment of tumor cells, gemcitabine, cancer prevention.
New Approach to Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Shows Promise for Survival
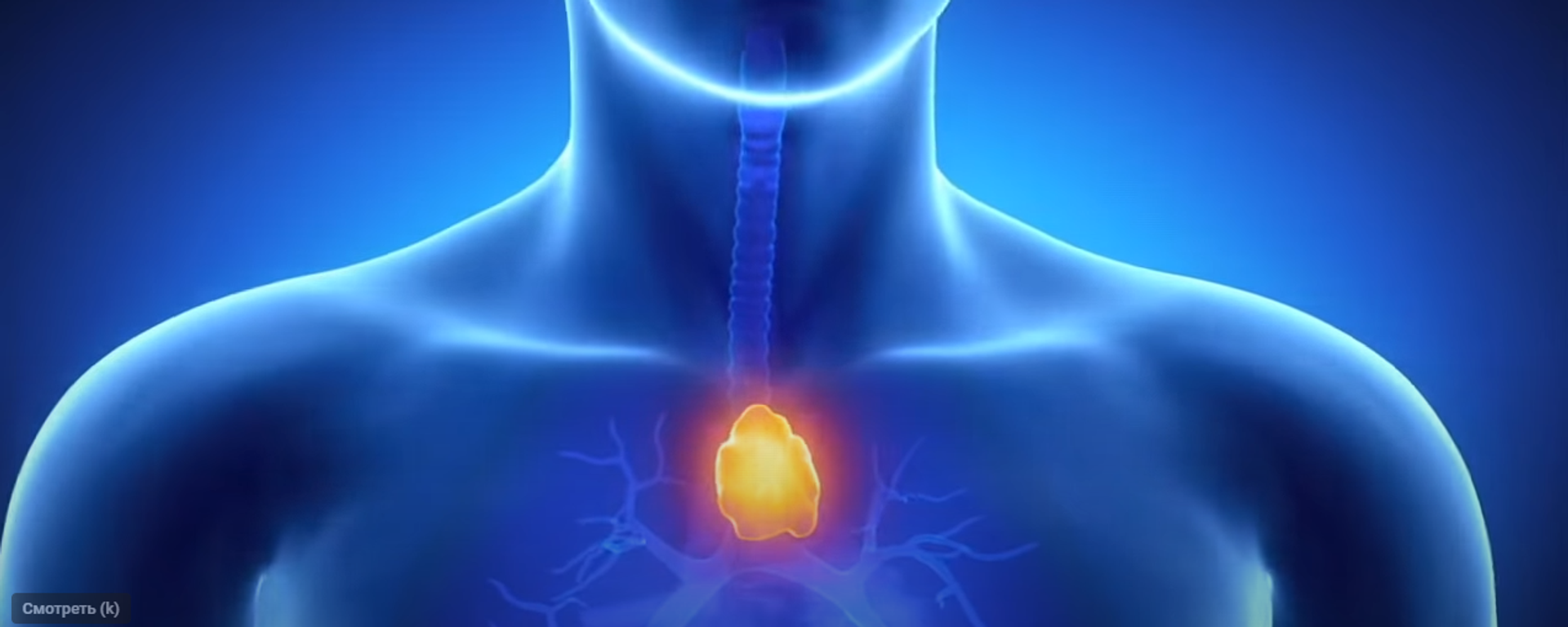
Pancreatic cancer is notorious for being very hard to identify and is often caught only after it has ceased to be treatable. This means that it has a particularly low survival rate, with only 12 percent of patients living for a year and 9 percent surviving for five years.
Preclinical studies conducted by the VCU Massey Comprehensive Cancer Center and the VCU Institute of Molecular Medicine in Virginia in the United States have demonstrated that polyinosine–polycytidylic acid (pIC), when directly administered to cancer cells, effectively inhibits tumor development and triggers malignant cell death.
This research was recently
published in the
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.
Mice with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumors, which closely mimic human pancreatic cancer, exhibited significantly improved survival rates after the implementation of a coordinated therapeutic plan. This promising approach, which harnesses the immune system offers hope for human pancreatic cancer patients.
The research show that pIC, a substance that boosts the immune system, increases the chances of survival in lab animals with pancreatic cancer. It's safe for normal pancreatic cells and might improve survival for people with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a type of pancreatic cancer, either when used alone or in combination with conventional treatments such as gemcitabine.
PDAC is known for being very hard to treat. It has a low survival rate, with only 12 percent of patients living for a year and just 9 percent surviving for five years. The research team established that a coordinated therapeutic plan significantly improved survival rates in mice with PDAC tumors, which closely resemble human pancreatic cancer. By using polyethyleneimine (PEI) to deliver pIC into the intracellular environment of tumor cells, the researchers have successfully stimulated cancer cell death.
15 August 2023, 21:38 GMT
The research found that pretreating mice with pIC before cancer development reduced tumor growth by approximately 60 percent, suggesting a potential protective, vaccine-like effect. Further research is needed to explore its implications for cancer prevention.
The study's promising results for treating pancreatic cancer suggest that this approach could potentially be used for various cancer types in conjunction with standard care.