One-Of-a-Kind Eclipse to Occur as Asteroid Leona Passes Over 'Betelgeuse' Star
04:02 GMT 11.12.2023 (Updated: 06:03 GMT 11.12.2023)
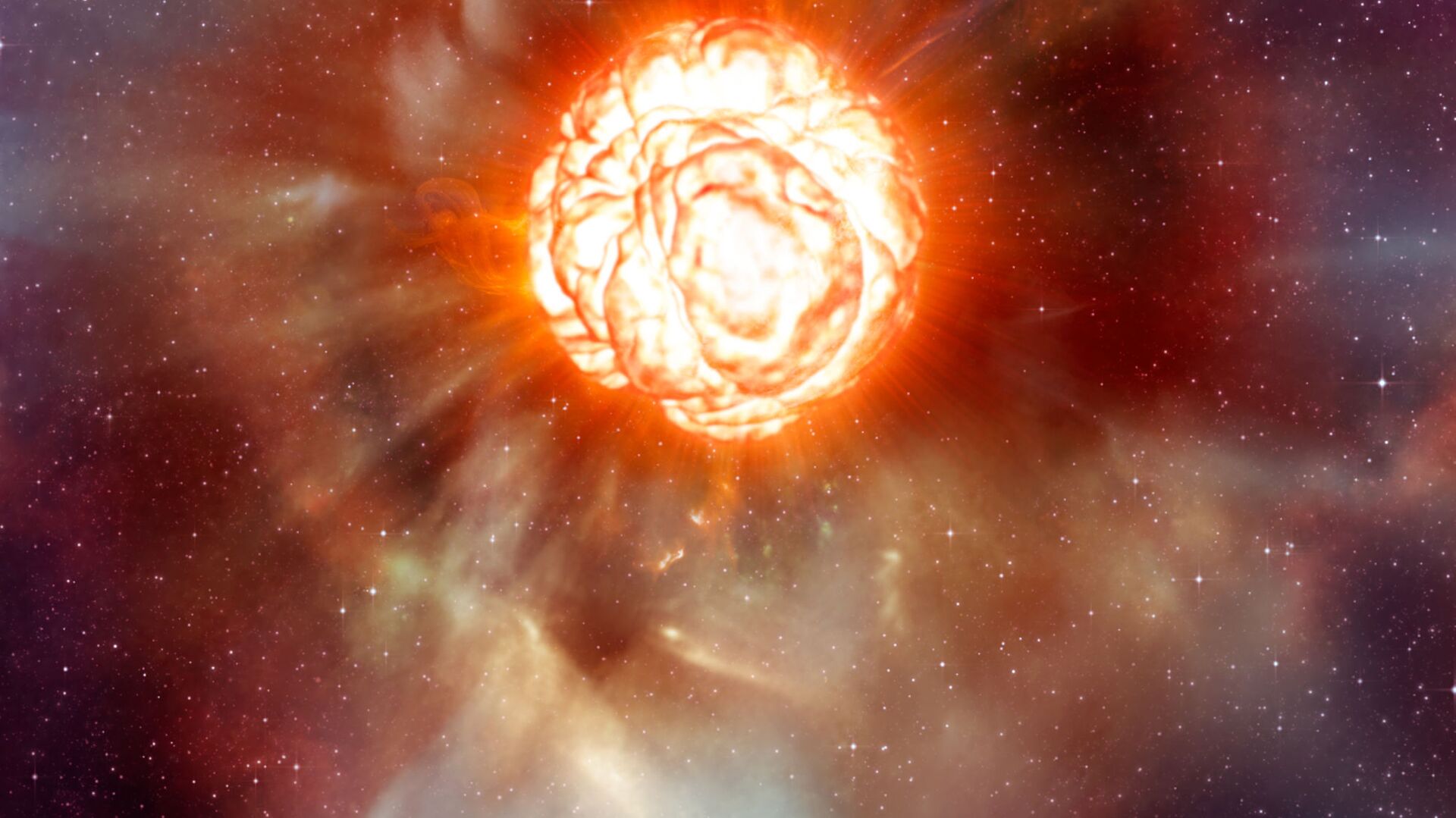

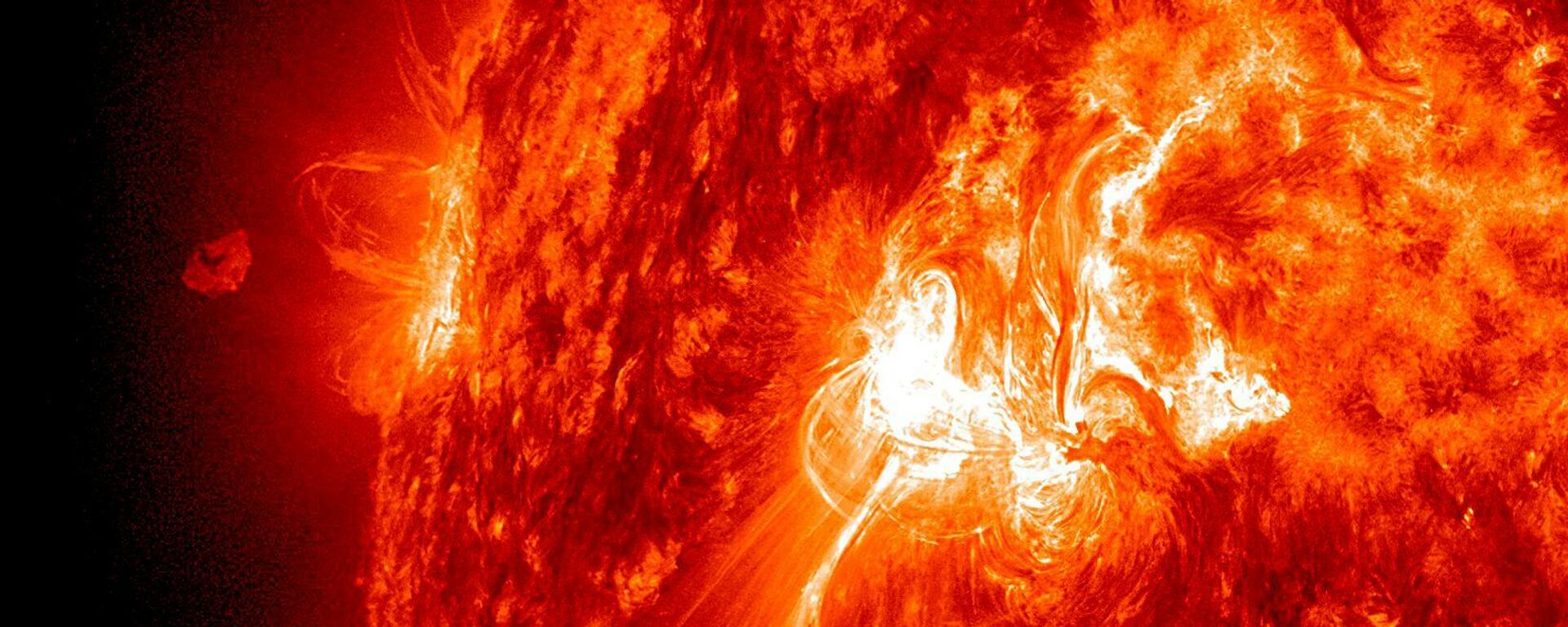
CC BY 4.0 / ESO/L. Calçada / A plume on Betelgeuse (artist’s impression)
Subscribe
Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star and belongs to the constellation Orion as the hunter’s “left shoulder”. It’s one of the brightest stars in the night sky, as well as one of the largest stars ever discovered, according to NASA.
What is expected to be a “one-of-a-kind” event will take place late Monday into early Tuesday: the eclipse of the star Betelgeuse as the asteroid Leona passes in front of it. Astronomers are even hoping to learn more about Betelgeuse and Leona during the eclipse, which could last anywhere from 10 to 15 seconds.
In September, astronomers observed a similar eclipse between Leona and a much dimmer star. They then estimated the asteroid to be about 34 miles wide and 50 miles long. But there are still some uncertainties regarding these predictions as well as the size of the star and its atmosphere.
"This kind of occultations are very useful to constrain the shape of the asteroid involved," Gianluca Masi, director of the Italy-based Virtual Telescope Project, said in a statement. "Here, we hope to even investigate the surface of the involved star, too: Betelgeuse. It is a large red supergiant and while Leona will move in front of it as seen from Earth, we will be hopefully able to learn more about its large convective cells, driving its variable brightness."
Betelguese is a red supergiant with a distinctive orange-red color that is visible to the naked eye. The star, which is nearing the end of its life, is 10 million years old and is significantly younger than Earth’s 5-billion-year-old Sun.
However, Betelguese is much more massive than the Sun, and so it is burning through its materials at a faster rate. In fact, it is so large that if it replaced the Sun, it would stretch beyond Jupiter, says NASA. In 2019 the star drastically dipped in brightness by about 60%, tricking astronomers into believing it had entered its "pre-supernova" phase - the stage before a star's death. But in 2020 it returned to its original brightness, cheating death and causing a mysterious stir for astronomers.
Leona, or asteroid 319, is a slowly rotating, oblong space rock that orbits between Mars and Jupiter in the outer reaches of the main asteroid belt. It orbits the sun every 2,300 days (6.30 years), coming as close as 2.68 astronomical units (AU) from the sun. Its closest orbit to Earth is 1.70 AU, which is an extremely wide distance considering one AU is about 150 million kilometers (93 million miles).
BREAKING NEWS, really.
— Virtual Telescope (@VirtualTelescop) December 4, 2023
Next 12 Dec., we will show you live, online, the extremely rare #occultation of #Betelgeuse ⭐️ by asteroid #Leona. One of the rarest astronomical events ever.
Join us from the comfort of your home here 👇👇👇https://t.co/fPADt2FKHi pic.twitter.com/AYUorYVrhR
The eclipse should be visible to those in Europe as well as Asia, and is expected to occur at 8:16 EST.