Poland’s Army ‘in Shambles’ Thanks to 90s Disarmament Overseen by NATO - Fmr General

© Sputnik / V. Kalinichev
Subscribe
Poland and its European allies in NATO have poured tens of billions of euros’ worth of military equipment and ammunition into the proxy war against Russia in Ukraine over the past two years, with little to show for it apart from drained armories and soaring profits for defense contractors.
The end of the Cold War and the 1992 Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE) severely weakened Poland’s defense capabilities, with Warsaw’s accession to NATO in 1999 apparently doing little to address the problem, retired Polish general Waldemar Skrzypczak has admitted.
“Under this treaty [the CFE, ed.] we were controlled by NATO countries. The treaty obliged us to reduce our military potential. We reduced the number of tanks, helicopters and howitzers,” Skrzypczak said in an interview with the Polish Press Agency on Monday, a day ahead of the 25th anniversary of Poland’s accession into the North Atlantic Alliance.
“In 1998, a delegation from [NATO’s] Rapid Reaction Corps visited us,” the former Land Forces commander recalled. “They stayed with us for 4-5 days and looked at basically everything, checking barracks infrastructure, the security of equipment, inspected the equipment – tanks, howitzers; at the time these were all Soviet. They watched how we train, how we organize training and what the relations are like between officers and soldiers,” Skrzypczak said.
After joining the bloc in March 1999, Poland’s military was forced to completely rework its thinking, down to definitions about the functioning of the army and various rules, regulations doctrinal matters, Skrzypczak said. “We gradually implemented…the requirements applicable in NATO. It was a completely different category of thinking and acting, so we had to completely change many things and learn some things from scratch.”
The rapid pace of “integration” allowed Poland to join the Americans during the 2003 invasion of Iraq, with Polish forces “proving” in that conflict and in Afghanistan that “we are efficient and well-prepared enough to meet any challenge they put before us.”
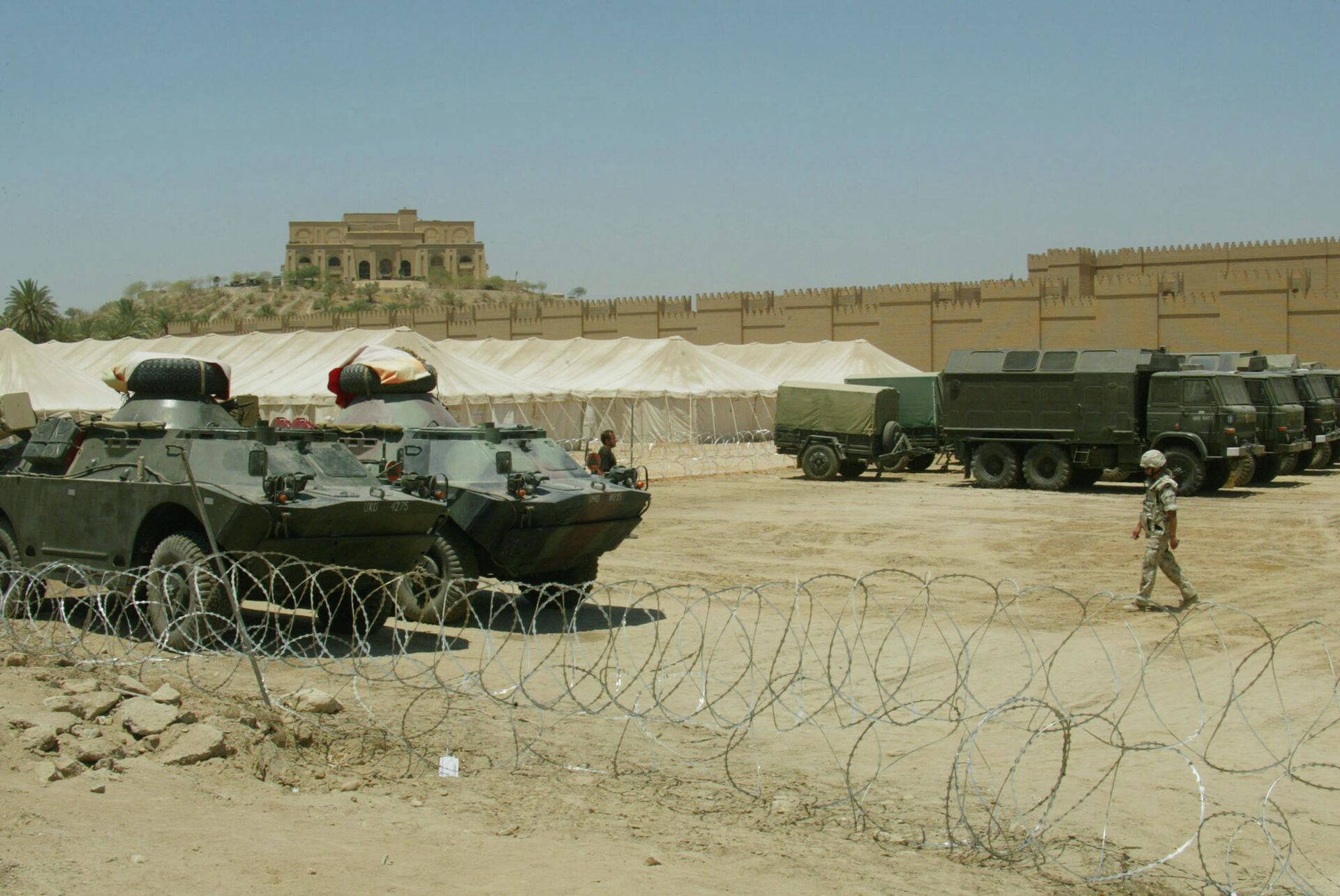

A Polish soldier walks back to his tent just outside the ancient City of Babylon, 80 km (50 miles) south of Baghdad, Iraq on Wednesday July 16, 2003. At least 23 Polish troops were killed in the conflict.
© AP Photo / Bullit Marquez
“The assessments given to our commanders by the Americans show that they assessed our skills, command efficiency and military very highly,” Skrzypczak suggested.
But only amid the Ukrainian crisis has the Polish military truly begun to move away from its post-WWII origins, the former general said. “Only now, after we have transferred a lot of equipment to Ukraine, and new equipment is set to appear in its place, will the army change completely.”
The transition will be difficult, according to Skrzypczak, because “right now there is no equipment and the [Polish] army is in shambles, like all European armies. The political will exists in NATO countries to [rearm] quickly, the processes are accelerating, everyone is increasing financial expenditures on military modernization, and so are we,” he stressed.
Poland will have to do 10 years-worth of modernization in 2-3 years because of the supposed “threat that may be lurking behind the eastern border,” i.e. from Russia, the retired general added.
Skrzypczak did not elaborate on why Russia, which was forced to watch passively over a quarter century as NATO expanded toward its borders, is such a “threat” to the Western alliance, and not the other way around.
While allied to the USSR from 1945-1990, Poland had one of the most powerful militaries in Europe, fielding nearly 350,000 troops, over 3,300 tanks, close to 4,900 infantry fighting vehicles, more than 80 tactical missile launchers and nearly 500 planes. The country also had major tank and shipbuilding capabilities thanks to a powerful industrial base. The end of the Cold War, the disintegration of the Warsaw Pact in February 1991 and the difficult transition to a market economy hit Poland’s defense capabilities hard, with the army shrinking and the production of domestically produced military equipment falling dramatically.
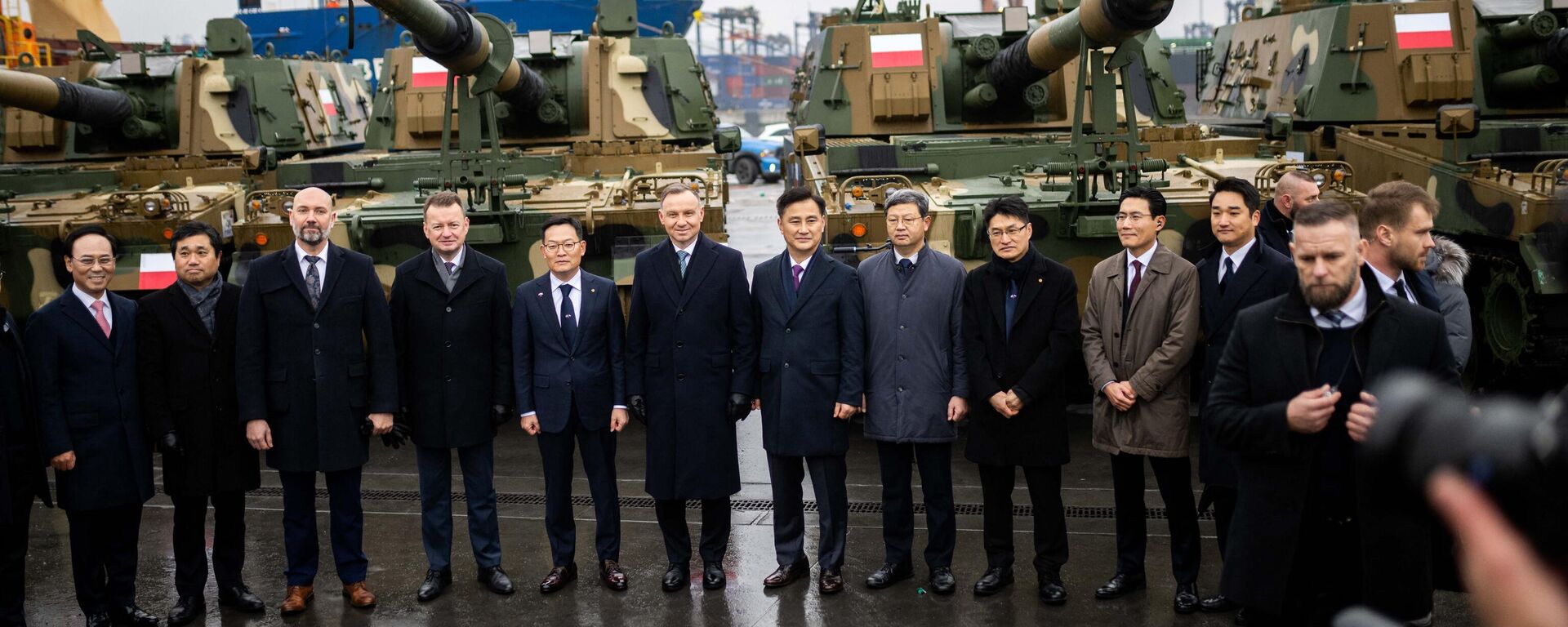
After sending some €3 billion worth of Soviet-era equipment to Kiev, Poland has been left highly dependent on assistance from its US allies, and on contracts with South Korea, when it comes to replenishing its stocks.
Aid to Kiev has included 14 Polish MiG-29 fighters, a dozen Mi-24 helicopter gunships, over 300 Soviet and Polish variants of the T-72 tank, 142 Polish-variant BMP-1s (known as BWP-1) and an array of sophisticated but aging Soviet howitzer and rocket artillery and air defense equipment.
The Polish Armed Forces today has about 200,000 active duty servicemen, with the government recently launching a large-scale rearmament program. Warsaw laid out about 97.4 billion zlotys (about $24 billion) for defense in 2023 – far outpacing a record $17.38 billion in spending set in 1977 – which shrunk to about $1.5-$2 billion through the 80s during the Polish crisis.
Polish officials have made a series of belligerent statements in recent days in connection with the Ukrainian conflict, with Polish Foreign Minister Radoslaw Sikorski suggesting Friday that the presence of NATO forces in Ukraine “is not unthinkable,” and adding Sunday that there are already alliance troops in the country, without elaborating.
Kremlin confirmed on Monday that Russia’s intelligence services “have long had information” on so-called NATO “advisers” present in Ukraine.
Italian Defense Minister Guido Crosetto rushed to walk back Sikorski’s comments on Sunday, saying “France and Poland cannot speak on behalf of NATO, which formally and voluntarily did not intervene in the conflict from the very beginning.” Crosetto warned that “sending troops to Kiev is a step toward unilateral escalation that will erase the path to diplomacy.”