The GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast (MOAB) is a large-yield conventional non-nuclear bomb considered to be the most powerful non-nuclear weapon ever developed at the time of its creation. The cost of a single MOAB is $16 million.
This was the first time the bomb was dropped in combat. It has been in service since 2003.
The Afghan Defense Ministry reported that at least 36 Daesh militants were killed in the bomb attack. However, later it was reported that 82 militants were killed as a result of the bomb drop.
Commenting on the US bomb strike, Sputnik contributor Andrei Kots noted that it has rather a "psychological effect."
"Honestly speaking, that was a blast. But if the potential enemy has a capable air-defense system, the GBU-43 will be useless, because a MC-130 would be taken down even before reaching the drop area," he wrote.
FOAB
The GBU-43 is not the heaviest bomb in history though. This is the GBU-57A/B Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP), a precision-guided 14,000-kg bunker buster bomb in service with the US Air Force.
The MOP can penetrate as deep as 60 meters under the ground and up to 19 meters of armored concrete. The first explosive test of the GBU-57 took place in 2007. The USAF received the first shipment of 20 bombs in 2011. The MOP has not been used in combat so far.
However, the most powerful non-nuclear bomb was developed in Russia. The Aviation Thermobaric Bomb of Increased Power (ATBIP) was field-tested on September 11, 2007.
It has a destructive power equivalent to 44 tons of TNT against 12 tons of TNT in the case of the GBU-43. It has a blast radius of over 300 meters compared to the MOAB’s 150-200 meters.
Information about the FOAB is secret, including the number of units produced and their deployment locations.
According to Russian military expert and journalist Viktor Murakhovsky, bombs with a destructive power equivalent to the MOAB were used by the Soviet Union during World War II.
According to the expert, in comparison to the GBU-43, the destructive radius of the US bomb is equal to the epicenter of the blast produced by the FOAB.
"On open terrain, the MOAB has a destructive radius of just 150-200 meters. At the same time, the FOAB produces a blast with an epicenter of 150-200 meters and its blast wave reaches beyond this area. The Russia bomb is destructive at a distance of up to 2.5 km," Murakhovsky told Sputnik.
Heavy Artillery
Heavy-caliber cannon artillery follows aviation bombs in terms of power, as well as absence in real combat conditions.
In the USSR, the 2s7 Pion 203-mm self-propelled cannon and its modification the 2s7 Malka were developed. Despite the fact that they were designed to fire special projectiles, several types of non-nuclear shells were developed. For example, the 110-kg 3FOF35 high-explosive projectile could be fired at a distance of up to 50 km.
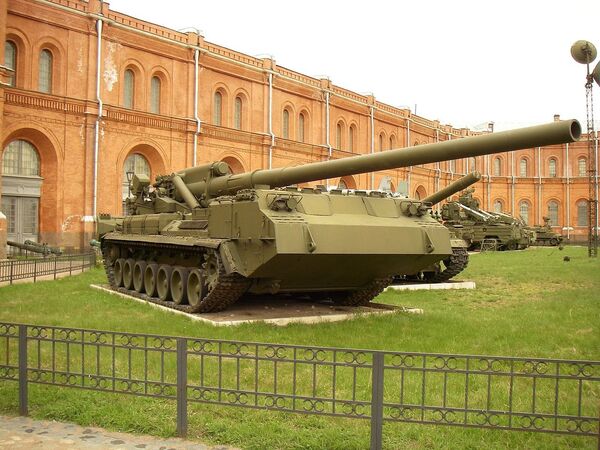

However, those weapons have significant disadvantages. There were few firing ranges where those artillery cannons could fire at medium and long distances. Moreover, both self-propelled cannons had small ammo reserves. Nevertheless, the Russian Armed Forces still have 300 Pion and Malka units, which have never been used in combat.
Western countries actively developed heavy-duty artillery systems in 1940-1945. Nazi Germany had the Karl 600-mm self-propelled mortars and the Dora 800-mm railway gun. In particular, they were used during the Great Patriotic War near Sevastopol and Brest Fortress.
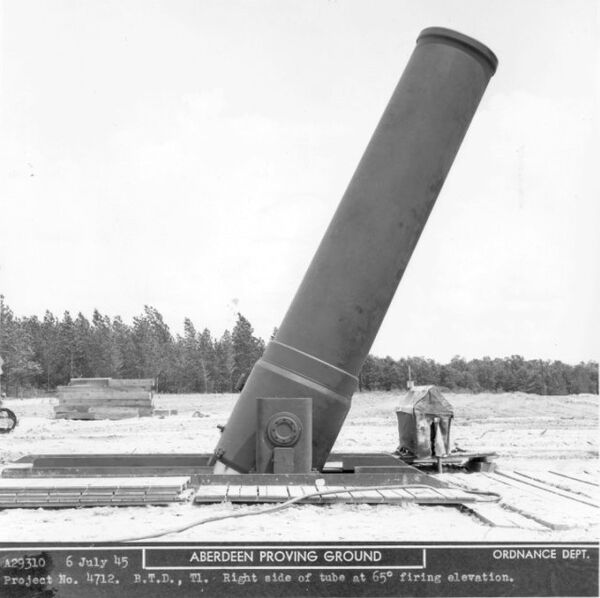

In 1944, the US tested the Little David mortar. It had a caliber of 914 mm and a weight of 88 tons. However, the cannon did not enter service.
'Caspian Monster'
During the Cold War, the Soviet military tried to develop an efficient weapon against US aircraft carriers. One of the most unusual developments was the Lun missile-carrying ekranoplan, some kind of a hybrid between a plane and a vessel.
It was a ground effect vehicle. It flew using the lift generated by the ground effect of its large wings when close to the surface of water.

The Lun had a length of 75 meters and a height of nearly 20 meters and could reach speeds of up to 500 kmh. American analysts dubbed the vehicle the "Caspian monster." The prototype was commissioned on July 16, 1986.
Because of an extremely low altitude, the Lun could bypass the air defenses on the enemy ship. It was expected to come close to the enemy aircraft carrier group and attack it with Moskit supersonic anti-ship missiles. Each missile had a 300-kg warhead and could travel at altitudes of 7-20 meters.
The only model of this class ever built, the MD-160, entered service with the Black Sea Fleet in 1987. It was retired in the late 1990s and is now sitting unused at a naval station in Kaspiysk.
Underwater Missile
The Shkval missile-torpedo is another Soviet-designed aircraft carrier killer with unique capabilities. It entered service with the Soviet Navy in 1977. Initially, it was armed with a 150-kiloton nuclear warhead, and then a conventional warhead was designed.
For decades, the Shkval was second-to-none among other torpedoes. However, in 2005, Germany said it had completed development of the Barracuda missile-torpedo capable of reaching the same speeds.
The Achilles’ heel of such weapons is its limited operation range. The Shkval is capable of hitting a target at a distance of only up to 13 km.
Never miss a story again — sign up to our Telegram channel and we'll keep you up to speed!