https://sputnikglobe.com/20220519/hedgehog-with-spikes-of-hot--cold-gas-revealed-during-solar-orbiters-historic-close-flyby-of-sun-1095630438.html
'Hedgehog' With Spikes of Hot & Cold Gas Revealed During Solar Orbiter's Historic Close Flyby of Sun
'Hedgehog' With Spikes of Hot & Cold Gas Revealed During Solar Orbiter's Historic Close Flyby of Sun
Sputnik International
The Solar Orbiter (SolO) – a joint effort of the European Space Agency and NASA – is a satellite on a mission to perform close observations of the Sun. During... 19.05.2022, Sputnik International
2022-05-19T11:16+0000
2022-05-19T11:16+0000
2023-04-12T16:59+0000
european space agency (esa)
nasa
orbiter
science & tech
sun
space
https://cdn1.img.sputnikglobe.com/img/07e6/05/13/1095627996_0:169:1920:1249_1920x0_80_0_0_1ea8ce8fae489716d2b5b850f9c445da.jpg
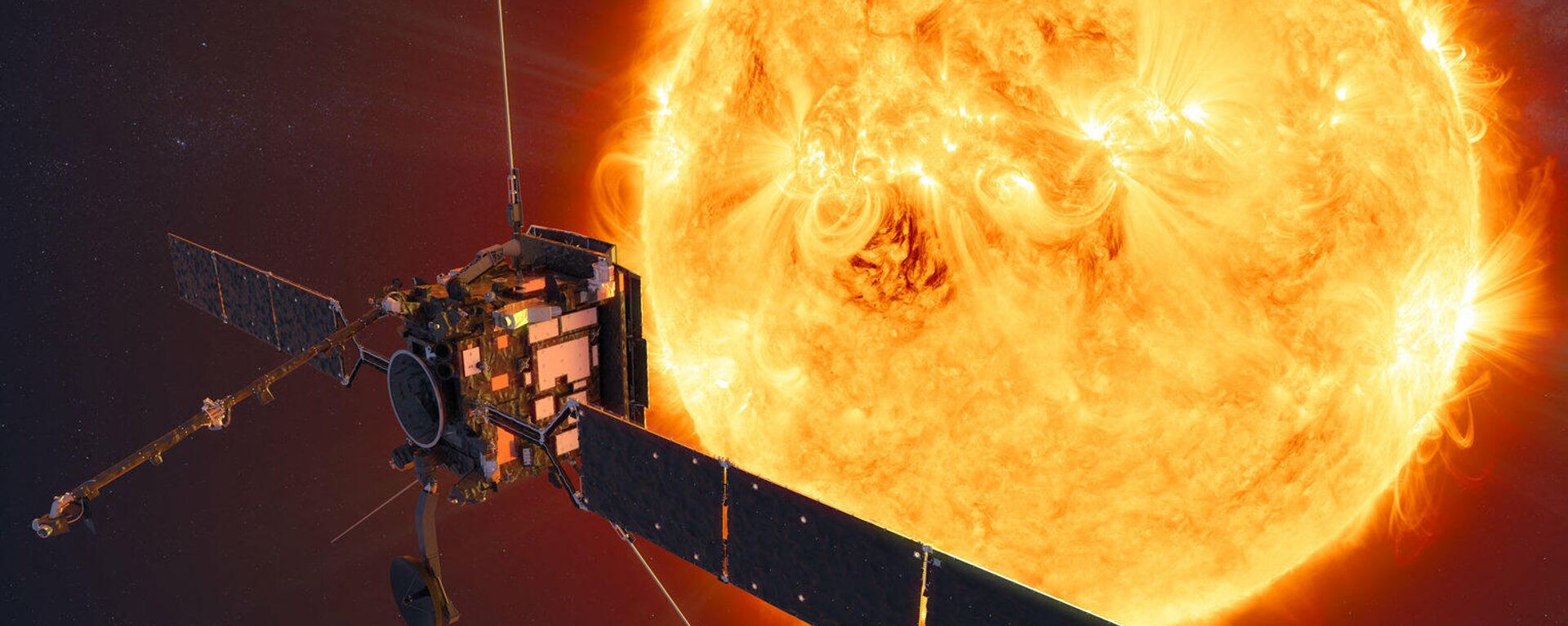
The Solar Orbiter (SolO) has offered up a stunning trove of new images of the Sun in its close encounter with the star on 26 March, which have now been released.After approaching within one-third the distance from the Sun to the Earth, the satellite, which is a joint effort of the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA, captured views of not only powerful solar flares and coronal mass ejections, but a new feature, nicknamed the "hedgehog".The unexpected feature stretches for around 15,534 miles (25,000 kilometres) on the Sun, emitting spikes of hot and cold gas. Scientists are currently unable to offer any explanation for what it is or how it formed in the Sun's atmosphere.During its flyby, the Solar Orbiter, which was launched on 10 February 2020 on a seven-year mission, functioned without a hitch despite the temperature of its heat shield reaching about 932 degrees Fahrenheit (500 degrees Celsius).The satellite is equipped with a multilayer heat shield, the special coating of which, called "Solar Black", is made using burnt bone. Furthermore, sliding doors protect its array of various instruments.SolO, along with another mission, called the Parker Solar Probe, is tailored to observe the Sun as it heads towards its “peak” activity. Once every 11 years, the Sun completes a solar cycle, with the current one - Solar Cycle 25 - officially having begun in December 2019.The next solar maximum activity is predicted to occur in July 2025.The Solar Orbiter’s tools allow it to obtain detailed measurements of the inner heliosphere and the solar wind, while also performing close observations of the polar regions of the Sun. This is something that is difficult to achieve from Earth, but the observations are important, as a deeper understanding of the Sun's behaviour and how it affects space weather helps scientists predict the impact on its Earth.The Sun’s space weather – along with eruptions like solar flares and coronal mass ejection events - can impact the power grid, satellites, GPS, airlines, and manned space missions.
https://sputnikglobe.com/20220511/scientists-claim-to-have-found-source-of-tiny-freckles-dotting-suns-surface-1095435099.html
https://sputnikglobe.com/20220219/solar-orbiter-captures-biggest-eruption-to-have-been-observed-on-the-sun-to-date---video-1093169079.html
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
2022
News
en_EN
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
european space agency (esa), nasa, orbiter, science & tech, sun, space
european space agency (esa), nasa, orbiter, science & tech, sun, space
'Hedgehog' With Spikes of Hot & Cold Gas Revealed During Solar Orbiter's Historic Close Flyby of Sun
11:16 GMT 19.05.2022 (Updated: 16:59 GMT 12.04.2023) The Solar Orbiter (SolO) – a joint effort of the European Space Agency and NASA – is a satellite on a mission to perform close observations of the Sun. During its first close approach in June 2020, at a distance of 48 million miles (77 million kilometres), it discovered miniature solar flares, dubbed “campfires” on the Sun.
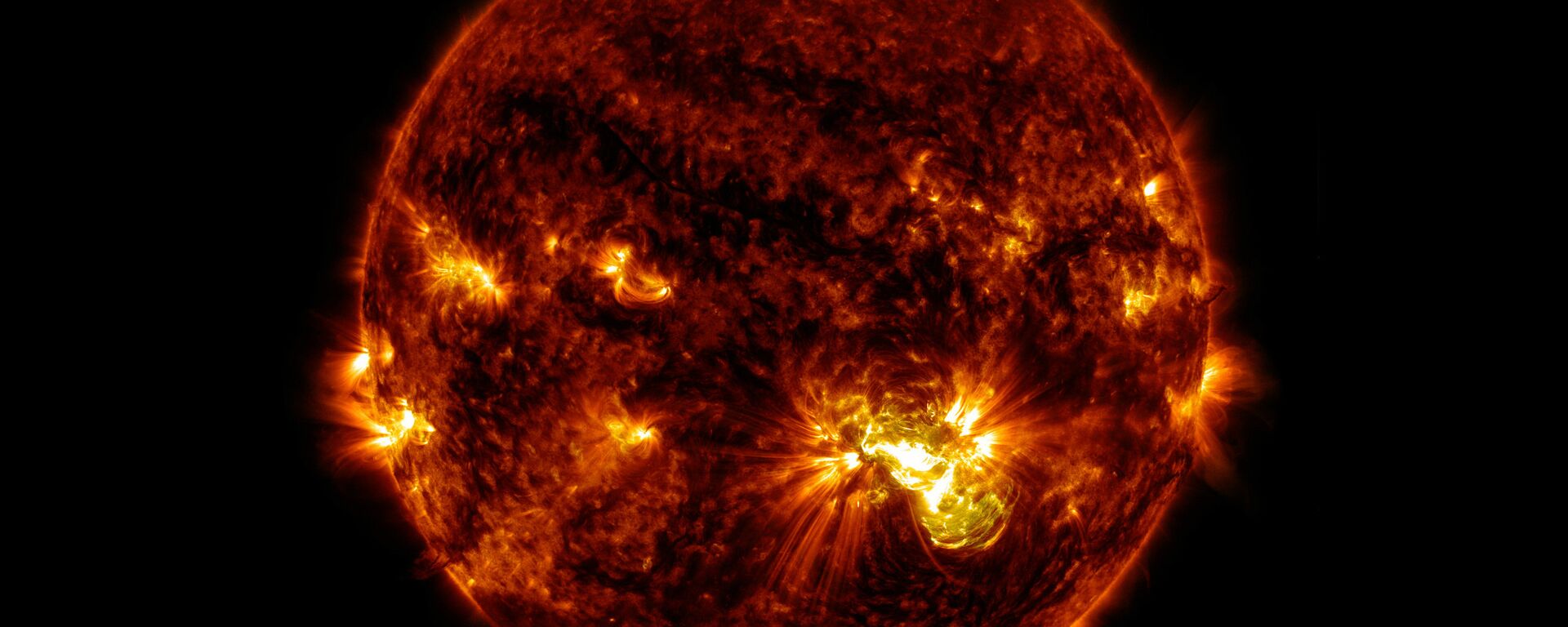
The Solar Orbiter (SolO) has offered up a stunning trove of new images of
the Sun in its close encounter with the star on 26 March, which have now been released.
After approaching within one-third the distance from the Sun to the Earth, the satellite, which is a joint effort of the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA, captured views of not only powerful solar flares and coronal mass ejections, but a new feature, nicknamed the "hedgehog".
The unexpected feature stretches for around 15,534 miles (25,000 kilometres) on the Sun, emitting spikes of hot and cold gas. Scientists are currently unable to offer any explanation for what it is or how it formed in the Sun's atmosphere.
During its flyby, the Solar Orbiter, which was launched on 10 February 2020 on a seven-year mission, functioned without a hitch despite the temperature of its heat shield reaching about 932 degrees Fahrenheit (500 degrees Celsius).
The satellite is equipped with a multilayer heat shield, the special coating of which, called "Solar Black", is made using burnt bone. Furthermore, sliding doors protect its array of various instruments.
SolO, along with another mission, called the
Parker Solar Probe, is tailored to observe the Sun as it heads towards its “peak” activity. Once every 11 years, the Sun completes a solar cycle, with the current one - Solar Cycle 25 - officially having begun in December 2019.The next solar maximum activity is predicted to occur in July 2025.
19 February 2022, 08:39 GMT
The Solar Orbiter’s tools allow it to obtain detailed measurements of the inner heliosphere and the
solar wind, while also performing close observations of the polar regions of the Sun. This is something that is difficult to achieve from Earth, but the observations are important, as a deeper understanding of the Sun's behaviour and how it affects space weather helps scientists predict the impact on its Earth.
The Sun’s space weather – along with eruptions like solar flares and coronal mass ejection events - can impact the power grid, satellites, GPS, airlines, and manned space missions.



