https://sputnikglobe.com/20230824/astronomers-detect-dark-spot-on-neptune-for-first-time-using-earth-based-telescope-1112869224.html
Astronomers Detect Dark Spot on Neptune for First Time Using Earth-Based Telescope
Astronomers Detect Dark Spot on Neptune for First Time Using Earth-Based Telescope
Sputnik International
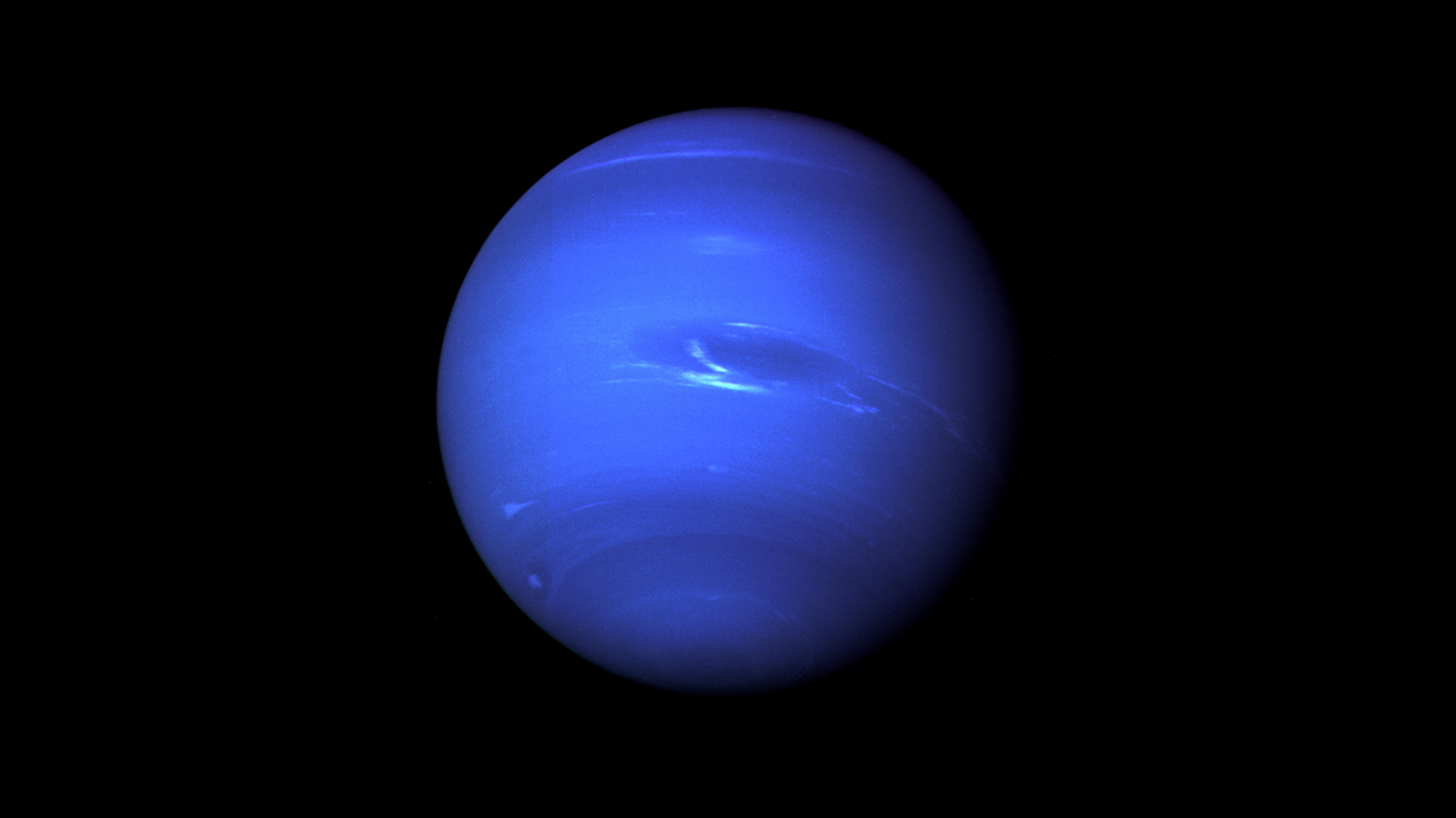
The solar system’s most distant plant, Neptune has remained an elusive object of study for astronomers since it was discovered in 1846. Very little was known about it until the Voyager 2 spacecraft flew past it in August 1989.
2023-08-24T21:09+0000
2023-08-24T21:09+0000
2023-08-24T21:08+0000
beyond politics
neptune
european southern observatory
astronomy
solar system
dark spots
https://cdn1.img.sputnikglobe.com/img/105620/08/1056200863_35:0:1159:632_1920x0_80_0_0_537fde6da3caa9960fa7c589e501043c.png
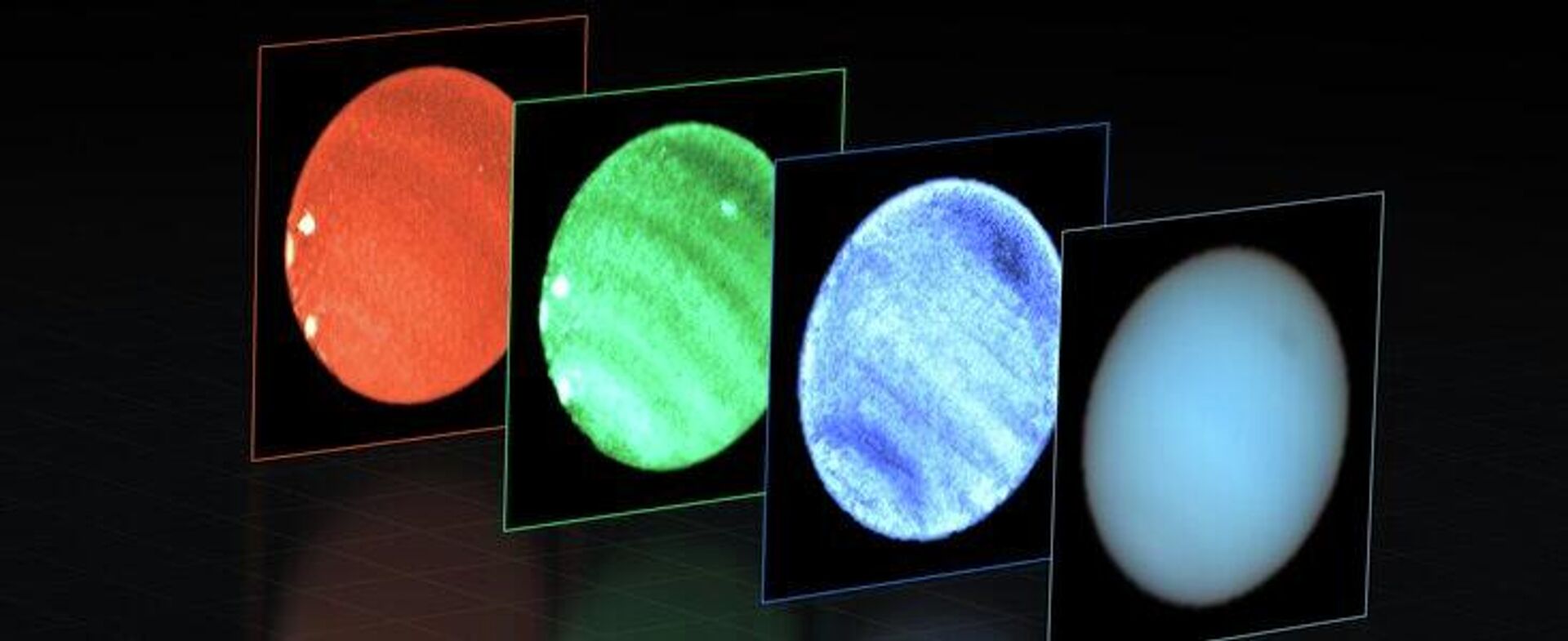
Astronomers at the European Southern Observatory (ESO) in the remote desert of northern Chile have announced a new first for humans on Earth: they managed to detect a “dark spot” on Neptune from Earth for the first time.When Voyager 2 flew past Neptune in 1989, it snapped photos of a massive “Big Dark Spot” on the planet, a massive storm analogous to Jupiter’s Big Red Spot. However, unlike Jupiter’s cyclone, Neptune’s has not persisted through the decades, disappearing and then reappearing again later.When the Hubble Space Telescope first observed Neptune after being launched in 1993, the dark spot was nowhere to be found. Only in 2018 did the Hubble finally see a new spot on Neptune.Now, however, astronomers spotted it from Earth."At first, we could only detect these spots by sending a spacecraft there, like Voyager. Then we gained the ability to make them out remotely with Hubble. Finally, technology has advanced to enable this from the ground."They made the discovery using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) and a device called the Multi-Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE), which allowed them to break up the sunlight reflected off the planet and enhance it, revealing the dark spot, according to an ESO news release.On frigid Neptune, 2.8 billion miles (4.6 billion kilometers) from the sun, the average temperature is negative 392 degrees Fahrenheit (negative 200 Celsius) and the atmosphere is made up by icy crystals of water, methane, and ammonia just as much as they are light gases like hydrogen and helium. However, the materials predominate at different levels of the atmosphere, with hydrogen and helium forming the majority of the upper layers and the icy contents being found deeper inside.Another study published just last week found a direct correlation between the sun’s regular cycle and the degree of cloud cover on Neptune, with cloud cover increasing on Neptune about two years after the solar maximum. The correlation provides strong evidence the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation might initiate a photochemical reaction in Neptune's atmosphere, leading to cloud formation, the scientists in Hawaii and California said.
https://sputnikglobe.com/20220922/fresh-james-webb-telescope-photo-shows-neptunes-rings-in-stunning-quality-1101066625.html
neptune
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
2023
News
en_EN
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
neptune; dark spot; european southern observatory; solar system
neptune; dark spot; european southern observatory; solar system
Astronomers Detect Dark Spot on Neptune for First Time Using Earth-Based Telescope
The solar system’s most distant plant, Neptune has remained an elusive object of study for astronomers since it was discovered in 1846. Very little was known about it until the Voyager 2 spacecraft flew past it in August 1989, snapping the first-ever up-close photos of the icy giant.
Astronomers at the European Southern Observatory (ESO) in the remote desert of northern Chile have announced a new first for humans on Earth: they managed to detect a “dark spot” on Neptune from Earth for the first time.
When
Voyager 2 flew past Neptune in 1989, it snapped photos of a massive “Big Dark Spot” on the planet, a massive storm analogous to Jupiter’s Big Red Spot. However, unlike Jupiter’s cyclone, Neptune’s has not persisted through the decades, disappearing and then reappearing again later.
When the Hubble Space Telescope first observed Neptune after being launched in 1993, the dark spot was nowhere to be found. Only in 2018 did the Hubble finally see a new spot on Neptune.

22 September 2022, 03:17 GMT
Now, however, astronomers spotted it from Earth.
"This is an astounding increase in humanity's ability to observe the cosmos,” said Michael Wong, a researcher at the University of California and a co-author of a study published in Nature Astronomy on Thursday.
"At first, we could only detect these spots by sending a spacecraft there, like Voyager. Then we gained the ability to make them out remotely with Hubble. Finally, technology has advanced to enable this from the ground."
They made the discovery using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) and a device called the Multi-Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE), which allowed them to break up the sunlight reflected off the planet and enhance it, revealing the dark spot, according to an
ESO news release.
Little is understood about such spots, which might be created by the mixing of gas particles from different layers of the planet.
On frigid Neptune, 2.8 billion miles (4.6 billion kilometers) from the sun, the average temperature is negative 392 degrees Fahrenheit (negative 200 Celsius) and the atmosphere is made up by icy crystals of water, methane, and ammonia just as much as they are light gases like hydrogen and helium. However, the materials predominate at different levels of the atmosphere, with hydrogen and helium forming the majority of the upper layers and the icy contents being found deeper inside.
Another study
published just last week found a direct correlation between the sun’s regular cycle and the degree of cloud cover on Neptune, with cloud cover increasing on Neptune about two years after the solar maximum. The correlation provides strong evidence the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation might initiate a photochemical reaction in Neptune's atmosphere, leading to cloud formation, the scientists in Hawaii and California said.