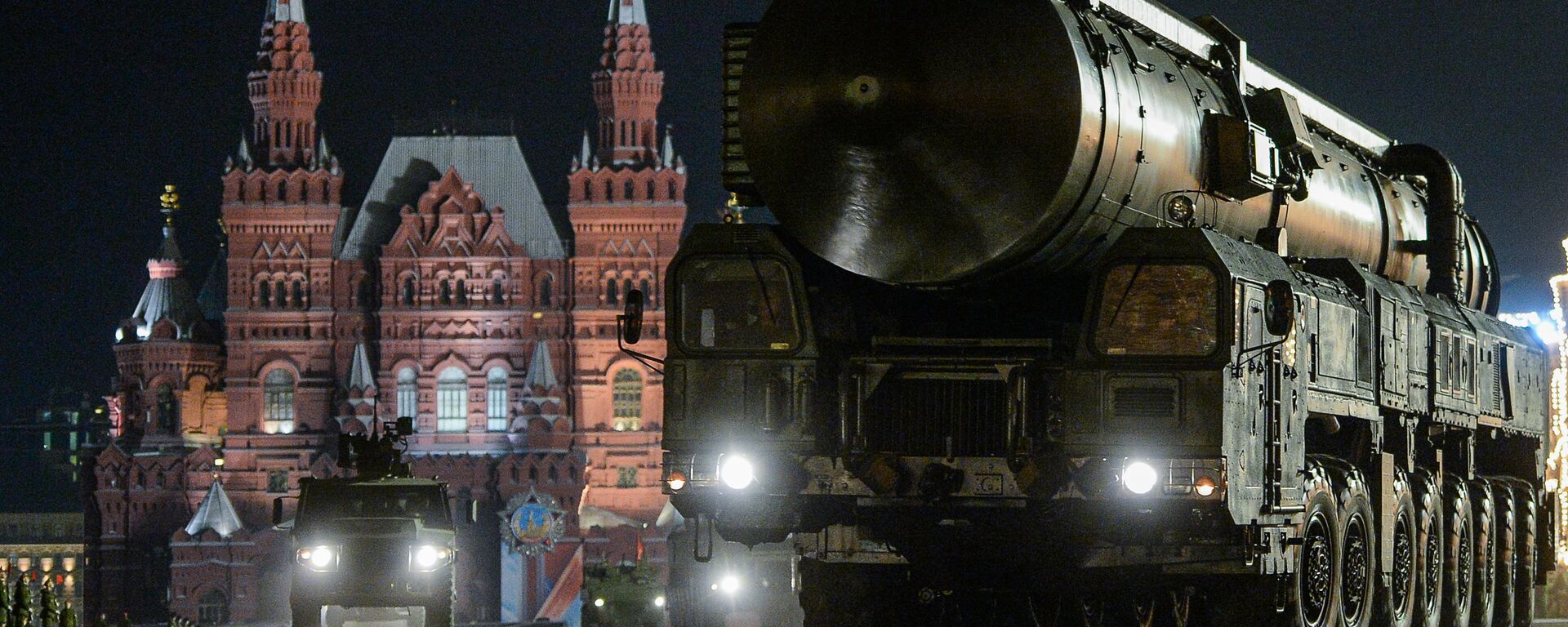https://sputnikglobe.com/20231223/us-may-forgo-deployment-of-antiquated-icbms-in-face-of-russias-avangard-missile-1115766416.html
US May Forgo Deployment of Antiquated ICBMs in Face of Russia's Avangard Missile
US May Forgo Deployment of Antiquated ICBMs in Face of Russia's Avangard Missile
Sputnik International
There is a growing possibility that the United States will be forced to give up the idea of deploying ground-based intercontinental range ballistic missiles Minuteman III entirely, Military Watch Magazine (MWM) reported.
2023-12-23T12:11+0000
2023-12-23T12:11+0000
2023-12-23T12:11+0000
military
russia
us
intercontinental ballistic missile (icbm)
icbm
icbms
avangard
yars missile
rs-24 yars
sarmat ballistic missile
https://cdn1.img.sputnikglobe.com/img/105692/90/1056929024_0:525:4014:2783_1920x0_80_0_0_7de9b3c31b6940b74271c73594c3bd6e.jpg
There is a growing possibility that the United States will be forced to give up the idea of deploying ground-based intercontinental range ballistic missiles entirely, Military Watch Magazine (MWM) reported.While Russia’s ground-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) force is deemed the most capable in the world, the outlet wrote, by contrast, the US has to rely on “the oldest ICBM class in the world.” America’s legacy Minuteman III – the land-based leg of the US' nuclear triad – is half a century old, and the US has struggled to develop a successor. The result is that the Minuteman III arsenal faces the prospect of decommissioning without replacement.One of the reasons for the discrepancy in this case between Russia and the US is that Washington has over-relied on submarine-launched ballistic missiles and nuclear bombers, the authors of the report underscored. Russia, on the other hand, opted to stake on ICBMs when building up its strategic nuclear strike capability.Russia has been expanding the number of RS-24 Yars mobile ground ICBM regiments in service with its Strategic Rocket Forces. The Yars system plays a crucial role in Russia's defense strategy. As older missile models are being replaced, the Yars, along with the RS-28 Sarmat, is set to become the backbone of Russia’s ground-based nuclear deterrent. Yars began to enter service from July 2010, and the first Sarmat unit went on combat alert in September.Sarmat, which has dozens of types of combat equipment that allow it to strike anywhere on Earth, boasts impressive range and destructive power, currently dubbed one of the deadliest nuclear missiles in the world.Furthermore, silo-based RS-18A missiles dating back to the Soviet era are being modified to carry Avangard hypersonic glide vehicles, the US outlet emphasized, reminding readers of the fact that the strike capability of the latter is unrivalled among other militaries.Russia, which once used to play catch-up against the United States, responded to the sharply heightened activity of NATO and US forces, including aircraft, being deployed near the country's borders. The Ukraine conflict has also served to incentivize Russia's modernization of its nuclear triad. Modern military equipment accounts for 95% of Russia's strategic nuclear forces, Russian President Vladimir Putin said while presiding over a Russian Ministry of Defense meeting on December 19.As for the LGM-30 Minuteman III, it is the third iteration of the Minuteman series of ICBMs, the first of which entered service in 1962. The missile was named after the famed “minutemen” militias of the American War of Independence. The Minuteman III, unveiled in 1970, could carry three nuclear warheads.Earlier in the year, there were reports that the replacement of the aging LGM-30G Minuteman III missile system with the Sentinel – estimated to cost $100 billion – had been delayed to a period between April and June 2030. Secretary of the US Air Force Frank Kendall disclosed that the LGM-35A Sentinel initiative was "struggling." The project was awarded to Northrop in 2020 under a $13.3 billion contract. The idea was to replace the aging LGM-30G Minuteman III missile system, as part of the US' $1.5 trillion nuclear modernization program, per sources. But the Sentinel project has been plagued by setbacks. Cost overruns could see the value of each missile rise by up to 50 percent from the 2020 estimate of $118 million, not adjusted for inflation. There have even been reports that an official review may potentially lead to the program's termination. It should be noted that while Russia has been actively modernizing its nuclear triad, unlike the US, its nuclear doctrine forbids the preemptive use of nuclear weapons of any kind –strategic or tactical, absent an enemy attack involving the use of nuclear weapons, or conventional aggression so severe it threatens the nation’s survival.
https://sputnikglobe.com/20231217/how-strategic-rocket-forces-saved-russia-from-being-erased-from-world-map-1115648163.html
https://sputnikglobe.com/20231219/putin-russian-nuclear-triad-is-95-modernized-1115677390.html
russia
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
2023
News
en_EN
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Sputnik International
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
minuteman iii, intercontinental ballistic missile, yars mobile complexes, yars mobile systems, russian forces, yars icbm, strategic missile forces, sarmat, russian nuclear, russia icbm, avangard hypersonic missile system,
minuteman iii, intercontinental ballistic missile, yars mobile complexes, yars mobile systems, russian forces, yars icbm, strategic missile forces, sarmat, russian nuclear, russia icbm, avangard hypersonic missile system,
US May Forgo Deployment of Antiquated ICBMs in Face of Russia's Avangard Missile
The development of Russia's Yars and Sarmat heavy strategic intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), along with the Avangard hypersonic missile system, has entirely changed the landscape of ground-based nuclear deterrent, a US publication has acknowledged.
There is a growing possibility that the United States will be forced to give up the idea of deploying ground-based
intercontinental range ballistic missiles entirely,
Military Watch Magazine (MWM) reported.
While Russia’s ground-based
intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) force is deemed the most capable in the world, the outlet wrote, by contrast, the US has to rely on “
the oldest ICBM class in the world.” America’s legacy
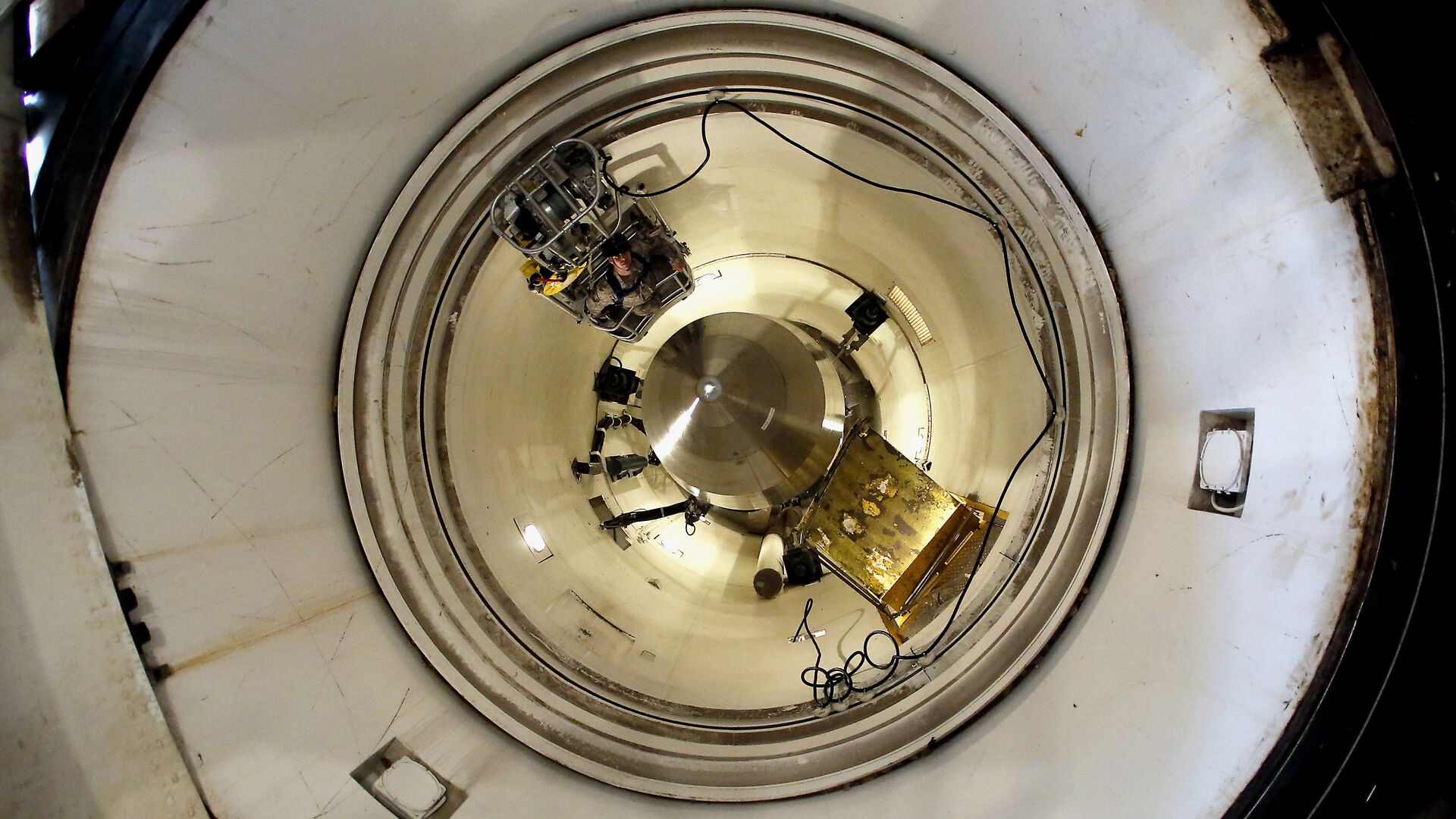
Minuteman III – the land-based leg of the US' nuclear triad – is half a century old, and the US has struggled to develop a successor. The result is that the Minuteman III arsenal faces the prospect of
decommissioning without replacement.
One of the reasons for the discrepancy in this case between Russia and the US is that Washington has over-relied on submarine-launched ballistic missiles and nuclear bombers, the authors of the report underscored. Russia, on the other hand, opted to stake on ICBMs when building up its strategic nuclear strike capability.
Russia has been expanding the number of
RS-24 Yars mobile ground ICBM regiments in service with its Strategic Rocket Forces. The
Yars system plays a crucial role in Russia's defense strategy. As older missile models are being replaced, the Yars, along with the
RS-28 Sarmat, is set to become the backbone of Russia’s ground-based nuclear deterrent. Yars began to enter service from July 2010, and the first Sarmat unit went on combat alert in September.
Sarmat, which has dozens of types of combat equipment that allow it to strike anywhere on Earth, boasts impressive range and destructive power, currently dubbed one of the deadliest nuclear missiles in the world.
Furthermore, silo-based RS-18A missiles dating back to the Soviet era are being modified to carry
Avangard hypersonic glide vehicles, the US outlet emphasized, reminding readers of the fact that the strike capability of the latter is unrivalled among other militaries.
The Avangard hypersonic missile complex is designed to neutralize the missile defense systems of potential adversaries. The complex features a hypersonic-guided warhead, and the missile itself can carry up to six nuclear warheads. It can reach speeds of more than Mach 27, which is almost 30,000 km/h.
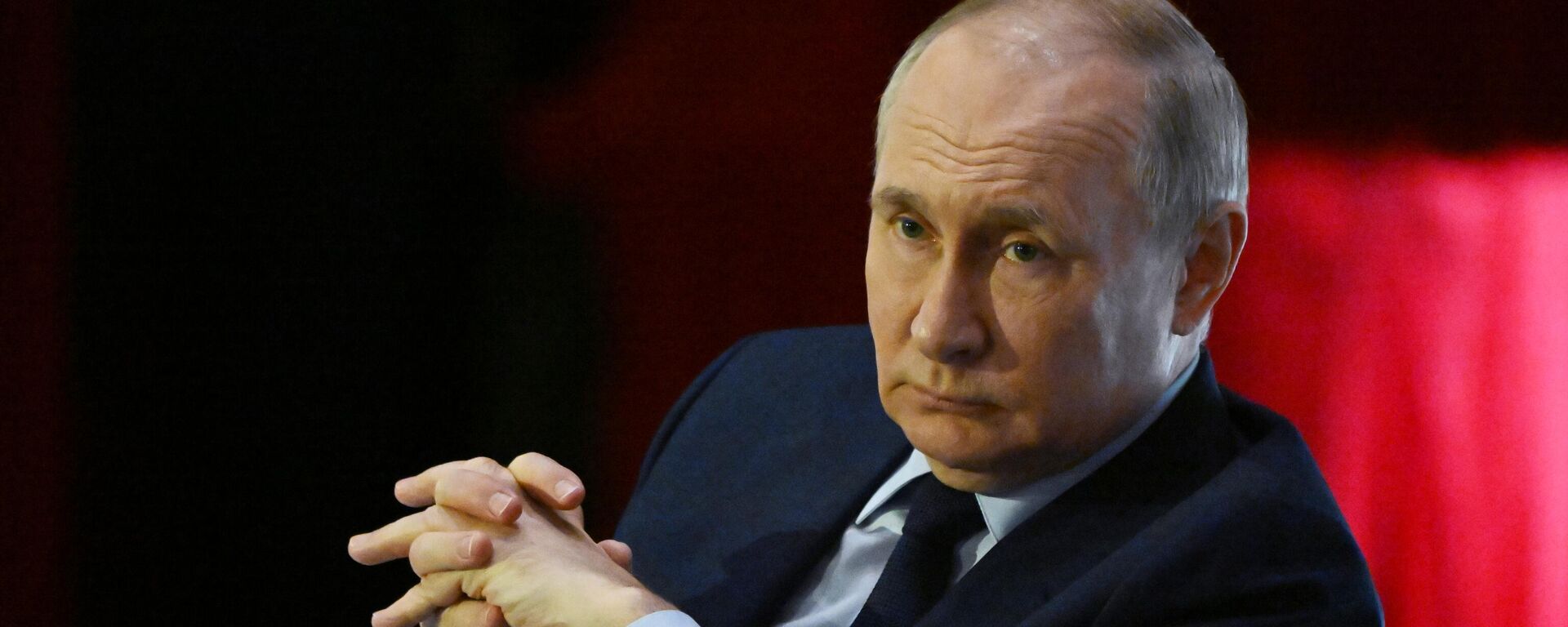
Russia, which once used to play catch-up against the United States, responded to the sharply heightened activity of NATO and US forces, including aircraft, being deployed near the country's borders. The Ukraine conflict has also served to incentivize Russia's modernization of its nuclear triad. Modern military equipment accounts for
95% of Russia's strategic nuclear forces, Russian President
Vladimir Putin said while presiding over a Russian Ministry of Defense meeting on December 19.
As for the LGM-30 Minuteman III, it is the third iteration of the Minuteman series of ICBMs, the first of which entered service in 1962. The missile was named after the famed “minutemen” militias of the American War of Independence. The Minuteman III, unveiled in 1970, could carry three nuclear warheads.
Earlier in the year, there were reports that the replacement of the aging LGM-30G Minuteman III missile system with the
Sentinel – estimated to cost $100 billion –
had been delayed to a period between April and June 2030. Secretary of the US Air Force
Frank Kendall disclosed that the LGM-35A Sentinel initiative was "
struggling." The project was awarded to Northrop in 2020 under a $13.3 billion contract. The idea was to replace the aging LGM-30G Minuteman III missile system, as part of the US' $1.5 trillion nuclear modernization program, per
sources. But the Sentinel project has been plagued by setbacks. Cost overruns could see the value of each missile rise by up to 50 percent from the 2020 estimate of $118 million, not adjusted for inflation. There have even been reports that an official review may potentially lead to the program's termination.
17 December 2023, 18:37 GMT
It should be noted that while Russia has been actively modernizing its nuclear triad, unlike the US, its
nuclear doctrine forbids the preemptive use of nuclear weapons of any kind –strategic or tactical, absent an enemy attack involving the use of nuclear weapons, or conventional aggression so severe it threatens the nation’s survival.

19 December 2023, 11:00 GMT